Pharmaceutical R&D Carrier opportunities explained with key roles, required skills, qualifications, career paths, growth opportunities, and FAQs to help you build a successful career in research and development.
Read MoreElectronic chemicals in the electronics industry explained with types, applications, semiconductor solvents, top manufacturers, and FAQs, highlighting their critical role in modern electronics and semiconductors.
Read MoreSpecialty Chemicals vs Commodity Chemicals explained with clear definitions, examples, applications, key differences, market trends, future outlook, and FAQs for industry professionals and students.
Read MoreLearn what an STP (standard test procedure) is, how to write it, key sections, safety considerations, calculation methods, typical chromatograms, applications, and a case study for accurate lab analysis and compliance.
Read MoreAnalytical Method vs Analytical Method Development explained with clear definitions, key differences, approaches, techniques, applications, and FAQs for pharmaceutical and analytical professionals.
Read MoreProduct validation in pharmaceuticals explained—definition, types, importance, validation process, regulatory compliance, and FAQs.
Read More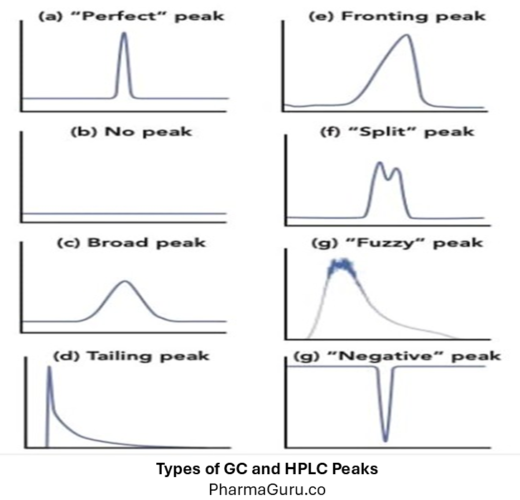
GC and HPLC peaks are graphical representations of compounds eluting from a chromatography system, where the x-axis denotes retention time, and the peak height or area corresponds to the compound’s concentration, providing both qualitative and quantitative information about the sample. Chromatography (both Gas Chromatography – GC and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography – HPLC) relies on the […]
Read More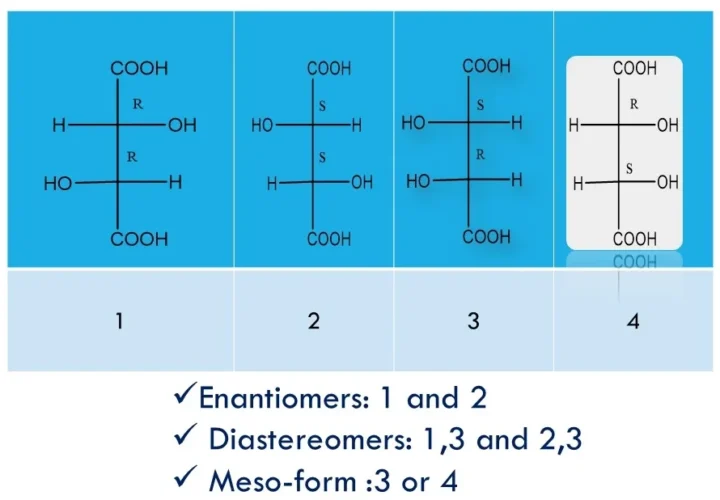
Enantiomers, diastereomers, racemates, and meso-compounds are types of stereoisomers—compounds with the same formula but different 3D arrangements—where enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images with opposite chirality, diastereomers are non-mirror-image stereoisomers with different properties, racemates are 50:50 mixtures of enantiomers that are optically inactive, and meso-compounds have chiral centres yet are achiral due to internal symmetry. Enantiomers, […]
Read MoreSwab sampling and Rinse sampling are key techniques in cleaning validation, each with distinct advantages. Guidelines recommend combining both methods for thorough residue assessment. Cleaning validation is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical manufacturing that ensures equipment and surfaces are free from residues of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), cleaning agents, and microbial contaminants. Two primary sampling […]
Read MorePartition, adsorption, ion exchange, and size exclusion chromatography are all powerful separation techniques and are widely used in pharmaceutical development. Partition chromatography separates components based on their relative solubility between two immiscible liquid phases. Adsorption chromatography relies on differences in how strongly compounds bind to a solid stationary phase. Ion exchange chromatography separates molecules according […]
Read MoreDenatured ethanol is ethanol that has been mixed with additives, such as methanol, to make it toxic and undrinkable. In contrast, undenatured or pure ethanol is the original, safe-to-drink form of alcohol. The main difference lies in the addition of these toxic chemicals, which prevents consumption as a beverage and makes denatured ethanol cheaper and […]
Read MoreAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the concentration of specific elements within a sample by measuring the amount of light absorbed by free atoms. In this method, the sample is first atomised—converted into gaseous atoms—after which light from an element-specific hollow cathode lamp passes through the vapour. The extent […]
Read MoreRaman spectroscopy and FTIR spectroscopy are both powerful vibrational techniques used to identify and characterise molecules, but they rely on different light–matter interactions. FTIR measures infrared light absorption caused by changes in a molecule’s dipole moment, while Raman detects inelastic scattering resulting from changes in polarizability. This fundamental difference makes them complementary methods—FTIR is more […]
Read More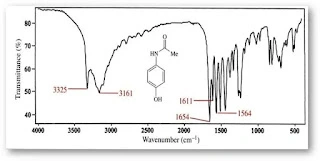
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to identify and analyze materials by measuring their absorption of infrared light. When IR radiation passes through a sample, its molecules absorb specific frequencies corresponding to their vibrational modes, producing a unique “molecular fingerprint” spectrum. This spectrum enables both qualitative and quantitative analysis of organic, […]
Read More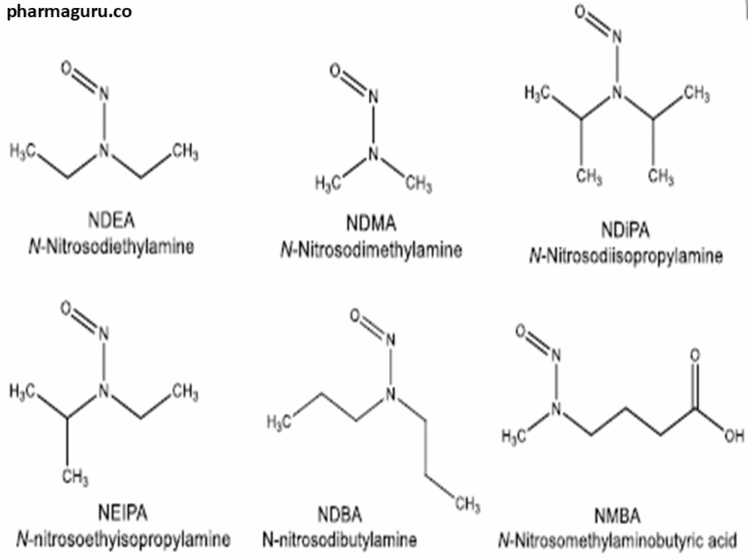
Nitrosamine Impurities and Analytical Waste must be managed in accordance with strict health, safety, and environmental regulations due to their carcinogenic properties. The primary and preferred disposal route is high-temperature hazardous-waste incineration, while chemical degradation approaches may be used only for lab-scale decontamination in authorised facilities. Related: What Is the TTC Concept and How Is It Related […]
Read MoreSynthetic drugs are artificially created in laboratories, while natural drugs are directly derived from sources like plants, animals, or microorganisms. Semisynthetic drugs begin with natural compounds that are chemically modified. The key differences lie in their origin, chemical structure, consistency, and regulatory control. Synthetic Vs Natural Drugs: FAQs You May Like: Synthetic Vs Natural Drugs: […]
Read MoreDrug discovery is the initial phase of identifying potential drug candidates by targeting a specific disease. Drug development is followed by testing the most promising candidates through preclinical and clinical trials to ensure safety, efficacy, and proper dosage before regulatory approval. The entire process is long, costly, and has a high failure rate. Drug Discovery […]
Read MoreNMR Interview Questions and Answers For R&D, Analytical, QC, QA, And RA Roles NMR interview questions typically cover both technical knowledge and soft skills. On the technical side, candidates may be asked about the principles of NMR, interpretation of spectra—such as chemical shift, spin–spin coupling, and multiplicity—along with the advantages, limitations, and applications of various […]
Read MoreInterview FAQs On FTIR And Uv Visible Spectrophotometer UV-visible and IR spectroscopy are widely used tools in pharmaceutical development for both qualitative and quantitative analysis. This is the reason why most of the questions are asked about these topics in pharmaceutical analytical or QC interviews. In this post, I will discuss all the questions asked […]
Read MoreTop titration interview questions often focus on the fundamentals, such as defining titration, distinguishing between the equivalence point and the end point, and explaining various titration types—including acid–base, redox, and complexometric methods. Candidates may also be asked about the principles behind specialised techniques like Karl Fischer titration, common sources of analytical error, and key concentration […]
Read MoreChromatography interviews typically focus on core principles, instrument components, and practical applications, along with essential skills such as method validation and troubleshooting. You can expect questions on separation mechanisms, the roles of the mobile and stationary phases, column types, detector principles, common system issues, and the advantages of GC. Gas Chromatography (GC) is widely used […]
Read MoreCommon HPLC interview questions typically focus on fundamental concepts such as the principle of HPLC, its instrumentation, column chemistry, and mobile-phase selection. Candidates are often tested on method development, system suitability parameters, and troubleshooting skills. You should be familiar with topics like retention time, normal-phase vs. reverse-phase chromatography, isocratic vs. gradient elution, and common issues […]
Read MoreHPLC method adjustment is necessary to ensure accurate pharmaceutical analysis, since factors such as analytical errors and environmental conditions can cause changes in retention time (RT), relative retention time (RRT), or peak shape. According to the standard test procedure (STP), analysis can not be initiated if the HPLC system fails in the system suitability test. […]
Read MoreGC method adjustment is often necessary during routine pharmaceutical analysis to achieve acceptable system suitability criteria and prevent failures caused by analytical errors. Analysis can not begin if the GC system fails in the system suitability test as per the standard testing procedure (STP). Now the question is, why does the GC system fail in […]
Read MoreChromatographic techniques are the backbone of pharmaceutical development. Pharmaceuticals development is impossible without the use of chromatographic techniques. However, most of the chemists don’t know why chromatographic techniques are widely used in pharma industries. That is why I decided to share my skill-based knowledge on ” Need for Chromatographic techniques”. Having read this article all […]
Read MoreHPLC column equilibration is the process of stabilising the column by fully saturating the stationary phase with the mobile phase, ensuring consistent backpressure, retention time stability, and a smooth baseline before injecting any sample. This is typically achieved by flushing the column with the mobile phase for a defined period—often around 60 minutes or at […]
Read MoreLearn everything about Karl Fischer titration for water determination in pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Explore its principle, procedure, reagents, reactions, applications, case studies, and FAQs.
Read MoreThe principle of TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography) is based on the differential affinity of components in a mixture toward a stationary phase and a mobile phase. As the liquid solvent (mobile phase) rises through the adsorbent layer—typically silica gel (stationary phase)—by capillary action, each component interacts differently with the two phases. Substances with a stronger […]
Read MorePDA (Photo Diode Array) Detector/DAD is a widely used technique to check the HPLC peak purity in the pharmaceutical industry due to its simplicity and fast result. In this article, you will learn about the peak purity concept, different methods for calculating peak purity, advantages, limitations, and applications of peak purity. You will also learn […]
Read More
The Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) concept and in silico assessment systems are powerful tools that help reduce the need for extensive toxicity testing of potential genotoxic impurities during pharmaceutical development. Managing genotoxic impurities is one of the most challenging responsibilities for pharmaceutical scientists, requiring a solid understanding of chemistry, toxicology, and regulatory expectations. In […]
Read MoreBoth Impurities And Related Substances degrade the quality of a pharmaceutical. Pharmaceutical impurities are unwanted substances found in a drug product, including residual starting materials, by-products, reagents, and degradation products. Related substances are a specific category of impurities that are structurally similar to the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), typically arising from the manufacturing process or […]
Read MoreBoth pKa and pH play a vital role at every stage during drug development. pH measures the acidity of a solution, whereas pKa reflects the intrinsic strength of an acid. pH can vary depending on the concentration of hydrogen ions in a particular solution, while pKa remains a constant characteristic of a specific acid at a […]
Read More
IPA (Isopropyl alcohol), or propan-2-ol(C3H8O)(C₃H₈O)(C3H8O), is a colourless, flammable liquid widely used as a solvent, disinfectant, and cleaner. Known for its rapid evaporation and ability to dissolve oils and greases, IPA is commonly employed in electronics cleaning, hand sanitisers, and industrial and household disinfection. Why 70% IPA is used in Pharma as Disinfectant? Isopropyl Alcohol […]
Read MoreIntroduction Selecting GC columns for alcohol analysis needs both knowledge of chromatography and expertise. Gas Chromatography (GC) is a powerful tool for analysing volatile compounds, and it’s especially useful for detecting and quantifying short-chain alcohols like methanol, ethanol, propanol, and their isomers. These alcohols are commonly found in pharmaceuticals, beverages, cosmetics, and industrial solvents—making accurate […]
Read MorePharmaceutical Conversions for Accurate Drug Dosing are vital for patient safety, as errors between metric, household, and apothecary systems can cause underdosing or toxicity. Precision in drug dosing can mean the difference between effective treatment and harmful side effects. This guide covers critical pharmaceutical conversions used in pharmacies, hospitals, and labs — presented in easy-to-read […]
Read MoreXRD analysis or X-ray diffraction analysis is a vital tool in pharmaceutical development, providing detailed insight into the solid-state properties of drug compounds. It is widely used to identify and quantify polymorphs, assess crystallinity, determine crystal structures, verify phase purity, and study drug–excipient interactions. As a non-destructive analytical technique, XRD delivers precise information about the […]
Read MoreWhile the ICH and ANVISA method validation guidelines share the same fundamental goal of ensuring reliability and accuracy, they differ in their level of detail and regulatory expectations. ANVISA generally adopts a more stringent approach, requiring the use of independent stock solutions for linearity assessments, more rigorous statistical analyses (including ANOVA and homoscedasticity testing), and […]
Read MoreParticle size analysis is a set of laboratory techniques to determine the size range and average size of particles in a sample, such as a powder or liquid. Common methods include sieving, sedimentation, laser diffraction, and microscopy. 1. What is Particle Analysis? Particle size analysis is the process of determining the size and distribution of […]
Read MoreUFLC vs UPLC vs HPLC: FAQs Related: Fast and Easy HPLC Column Equilibration Tips: Learn in 5 Minutes (With Case Studies & FAQs) What Is TLC (Thin-Layer Chromatography) And How Is It Useful for Quick Drug Identification And Reaction Monitoring? 8. Why is UFLC sometimes more practical than UPLC? UFLC offers a balance between speed […]
Read MoreBoth amorphous and crystalline drugs play distinct and important roles in pharmaceutical formulation, particularly in terms of stability, bioavailability, solubility, and dissolution. Crystalline drugs possess a well-ordered, stable molecular structure that results in slower dissolution and lower solubility, whereas amorphous drugs, lacking a defined lattice arrangement, exhibit higher solubility and faster dissolution rates but are […]
Read MorePolymer morphology and crystallinity are fundamental concepts that bridge molecular structure with the pharmacological performance of drug delivery systems. Polymer morphology studies the arrangement of polymer chains—whether amorphous (disordered), crystalline (ordered), or semi-crystalline (partly ordered). The degree of crystallinity determines key properties such as strength, stiffness, and density, and is influenced by factors like chain […]
Read MoreAn Uv Visible Spectrophotometer is an analytical instrument that measures the absorbance or transmittance of a sample across the ultraviolet and visible light spectrum (typically 200–800 nm). By passing a beam of light through a sample and detecting the absorbed or transmitted intensity it enables the identification and quantification of substances in liquids or solids. […]
Read MoreCustom API synthesis, especially within the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, involves the tailored design and production of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or other chemical compounds to meet precise client specifications. Unlike the large-scale manufacturing of generic compounds, this process emphasises customising the synthesis to achieve specific molecular structures, purity levels, quantities, and functional properties. Custom […]
Read MoreDiscover the most effective water treatment chemicals for hard water removal — including coagulants, flocculants, chlorine, alum, and antiscalants — to ensure clean, corrosion-free water for industrial and domestic use.
Read MoreBoth CROs and CMOs play crucial roles in drug development in the pharmaceutical industry. CROs focus on research activities such as clinical trial design, regulatory support, and data analysis, while CMOs specialise in the large-scale manufacturing of drug substances and finished products. A third type, the CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organisation), combines both functions—offering […]
Read MorepH meter is the backbone of drug development, because without accurate pH measurement, the quality and safety of neither raw materials, intermediates, nor active pharmaceutical ingredients, nor pharmaceutical formulations can be guaranteed. pH Meter: The Backbone of Drug Development 1. How pH Meter is the Backbone of Drug Development The pH meter plays a vital […]
Read MoreA Reference Standard (RS) is a highly purified, officially recognised substance that serves as the “gold standard” for identity, strength, quality, and purity in pharmaceutical analysis. In contrast, a Working Standard (WS) is a secondary standard, derived from and rigorously calibrated against the RS. While both are essential to maintaining the accuracy and reliability of […]
Read MoreDegradation products are a type of impurity formed when a substance chemically breaks down over time due to factors like heat, light, or moisture. While all degradation products are impurities, not all impurities are degradation products—some arise from manufacturing, excipients, or environmental contamination. Degradation Vs Impurities: FAQs You May Like: Degradation Vs Impurities: Key Differences […]
Read More
Tautomerism in pharmaceuticals refers to the interconversion of structural isomers via the migration of a hydrogen atom, while rotamerism involves the interconversion of conformational isomers through rotation around a single bond. Both processes can profoundly influence a drug’s stability, bioavailability, and pharmacological activity, with tautomeric transitions typically requiring a higher energy barrier than rotameric changes. […]
Read More
Sample preparation for HPLC analysis involves converting the sample into a clear, soluble solution at an appropriate concentration for injection. Techniques such as sonication, stirring, dissolution, filtration, and solvent extraction are employed to dissolve the sample, remove impurities, simplify complex matrices, and protect the HPLC column. The chosen method depends on the sample matrix, analyte […]
Read More
Pharmaceutical specifications define the quality standards a drug product must meet, including acceptance criteria and referenced test methods. Pharmaceutical tests are the laboratory procedures used to measure product characteristics and verify compliance with these specifications. In short, specifications describe what quality is required, while tests define how that quality is measured. Pharmaceutical Specifications vs Pharmaceutical […]
Read More
Photostability and forced degradation studies are stress-testing methods used in drug development to understand degradation pathways. Forced degradation uses extreme conditions (e.g., heat, pH, oxidation, light) to identify all potential degradation products and support stability-indicating method development. Photostability, a specific subset, focuses solely on light exposure to assess photosensitivity and determine the need for light-protective […]
Read More
Route of Synthesis (ROS) In Pharmaceutical Development: Interview Questions What is the API route of synthesis? he API Route of Synthesis refers to the detailed sequence of chemical reactions and processes used to produce the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) from basic starting materials or intermediates. Key Points: What is a route scouting? Route scouting is […]
Read More
A pharmaceutical dosage form is the final physical presentation of a drug, containing both the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients, with the API providing the therapeutic effect and excipients aiding in the formulation, stability, and delivery. Pharmaceutical Dosage forms, Excipients and APIs: Key Differences Aspect Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Excipients Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) Definition […]
Read MorePharmaceutical intermediates are chemical building blocks used in the multi-step synthesis of APIs—the active drug components that provide therapeutic effects. Unlike APIs, intermediates are not administered to patients, have no therapeutic effect, and are subject to less stringent regulations. However, their quality directly impacts the safety and efficacy of the final API. Pharmaceutical Intermediates vs […]
Read More
Classification of Analytical Methods is based on classical (wet chemistry, e.g., titration, gravimetry) and instrumental (e.g., spectroscopy, electrochemistry), and by their goals: qualitative (identifying substances) and quantitative (measuring amounts). Separation techniques, like chromatography, form a key category used to isolate components before analysis. Classification Of Analytical Methods For Pharmaceutical Analysis: Learn with 7+FAQs You May […]
Read More
Both C18 and C8 HPLC columns are the heart of the pharmaceutical analysis due to their longer life, wider applications, better selectivity and high theoretical plate. The C8 column (Octyl column) is a reversed-phase chromatographic column with an 8-carbon alkyl chain bonded to a silica support, used in HPLC for separating compounds based on hydrophobicity. […]
Read More
Related substances and assay tests are critical quality control measures in pharmaceuticals. The related substances test detects and quantifies impurities, while the assay test measures the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content. Together, they ensure the drug’s purity, potency, safety, and overall quality. Related Substances vs Assay Test in Pharmaceuticals: Key Differences Parameter Related Substances Test […]
Read More
Both SOP and STP play a vital role in maintaining the quality, safety and efficacy of a pharmaceutical in the pharmaceutical industry. An SOP (Standard Operating Procedure) outlines general instructions for routine tasks, ensuring consistency and efficiency. In contrast, STP refers Standard Testing Procedure related to the method of analysis. While the SOP provides the […]
Read More
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are the biologically active components of a drug responsible for its therapeutic effect. They are synthesised from raw materials through complex chemical processes. In the final drug product, APIs are combined with excipients—inactive substances that aid in the delivery and stability of the drug but have no therapeutic effect Active Pharmaceutical […]
Read More
Both the melting point and the boiling point play crucial roles in pharmaceutical analysis. The melting point is primarily used to identify and assess the purity of solid drug compounds, indicating the temperature at which a solid substance transitions to a liquid. In contrast, the boiling point applies to liquid drugs, defining the temperature at which a liquid […]
Read MoreColumn Chromatography: Interview Questions What are the different steps involved in column chromatography? The key steps involved in column chromatography are: What-are-the-problems-associated-with-column-chromatography? The following are 12 common problems associated with column chromatography: 1. Sample Overloading 2. Poor Resolution 3. Flow Rate Issues 4. Uneven Packing 5. Solvent Selection 6. Column Contamination 7. Back Pressure 8. […]
Read More
The drug development process is a rigorous, multi-phase journey that includes: Discovery and Preclinical testing to identify and evaluate potential drugs in labs and animals; Clinical Research (Phases 1–3) to assess safety, dosage, and efficacy in humans; FDA Review for regulatory approval based on all collected data; and Post-Market Monitoring to ensure long-term safety and […]
Read MorePreparative HPLC Vs Analytical HPLC: Key Differences Parameter Preparative HPLC Analytical HPLC Purpose To isolate and purify large quantities of a compound Quality control, method development, and content analysis Sample Size Large (milligrams to grams) Small (micrograms to milligrams) Column Size Larger diameter and longer columns (e.g., 10–50 mm ID) Smaller diameter and shorter columns […]
Read MoreThe Lessons Learned approach is a structured process of capturing, analysing, and applying insights from past successes and failures to enhance future projects and prevent the recurrence of mistakes. In the highly regulated and innovation-driven pharmaceutical development, mistakes can be costly, not just financially, but in terms of time, compliance, and patient safety. That’s why […]
Read MoreLearn Starting Material and Key Starting Material, definition, key differences, and case studies with FAQs
Read MoreLearn what a Stability Indicating Method (SIM) is in pharmaceutical analysis, why it's essential, key development steps, regulatory guidelines, and its advantages for ensuring drug safety and efficacy
Read More. Normality and Molarity measure solution concentration, but they’re not the same. Normality measures the concentration of reactive units (equivalents) per litre of solution, whereas Molarity measures the number of moles of solute per litre of solution What Is Difference Between Normality and Molarity? Feature Molarity (M) Normality (N) Definition Moles of solute per liter […]
Read More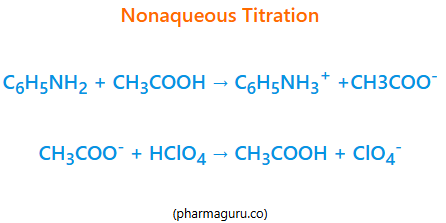
Learn nonaqueous titration—definition, working principle, key applications in pharmaceuticals, and a real-world case study. Ideal for students, researchers, and lab professionals.
Read MoreIn Complexometric titration, complex formation takes place during the titration. A typical example is EDTA titration. Several titration techniques are used in the pharmaceutical industry, and one them is EDTA titration. It plays a key role in determining metal ion concentrations. This method is highly valued for its specificity, accuracy, and applicability across a range […]
Read MoreA redox titration is an analytical technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown substance by reacting it with a precisely known volume of a standard solution in a redox reaction, where electron transfer occurs. It is also called reduction-oxidation titration. Unlike typical acid-base titrations, redox titrations deal with the transfer of electrons between […]
Read MoreAcid-base titration is commonly used to determine the concentration of an unknown acidic or basic substance through acid-base reactions. It is one of the most fundamental and widely used techniques in pharmaceutical development. This process involves determining the concentration of an unknown acid or base by neutralising it with a solution of known concentration, usually […]
Read MoreGC method validation for impurity analysis ensures the gas chromatography method is reliable and suitable for accurately, precisely, and specifically quantifying impurities in a sample Gas Chromatography (GC) plays a crucial role in controlling volatile impurities in pharmaceuticals. In this article, I will discuss how GC methods are validated for the quantitative determination of impurities […]
Read MoreHPLC solvents are liquid compounds used as part of the mobile phase to carry analytes through the column. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is one of the most widely used analytical techniques in pharmaceutical development. It is used for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a mixture. Solvents play a crucial role in this process, as […]
Read MoreIsocratic elution and Gradient elution are two fundamental modes of mobile phase composition control in HPLC. In HPLC, isocratic elution maintains a constant mobile phase composition throughout the separation, while gradient elution involves progressively changing the mobile phase composition during the run. Gradient elution is typically preferred for complex mixtures with components that have a […]
Read MorepKa in Reverse Phase HPLC governs peak elution. It plays a unique and critical role in the separation of analytes as it directly influences selectivity
Read MorepH plays a crucial role in the retention and separation of ionizable compounds in HPLC. By adjusting the mobile phase’s pH, analysts can control the ionisation state of analytes—whether acidic or basic—which directly influences their interaction with the stationary phase and ultimately their elution time. This allows precise control over the separation of compounds with […]
Read MoreLearn how RFT improves efficiency, reduces costs, and accelerates time-to-market by ensuring quality and accuracy at every stage of the process.
Read MoreLearn how Quality by Design (QbD) enhances pharmaceutical development by integrating quality into every stage. Explore its benefits, challenges, and real-world applications in ensuring safe, effective, and consistent drug products.
Read MorePotency and purity play a vital role in pharmaceutical analysis in managing quality, safety and efficacy of a pharmaceutical. Purity is the qualitative content of any drug substance or its phases, while potency is the absolute quantitative content of any drug substance or its phases. Potency and Purity Purity Purity is the qualitative content of […]
Read More
Both Hold Time Study and Stability Study assess product quality over time but they differ significantly in scope, purpose, and timing within the manufacturing lifecycle. Major Takeaway What is a Hold Time Study? A Hold Time Study is a validated study conducted to determine the acceptable time period during which in-process materials, intermediates, or bulk […]
Read MoreBoth Assay and Potency play a vital role in controlling the quality, safety and efficacy of a pharmaceutical. Assay is the quantitative relative content of a drug, while potency is the quantitative absolute value of a drug standard Assay and Potency Assay The Assay is the quantitative relative content of a pharmaceutical. It is a […]
Read MoreBoth Assay and Purity play a unique role in controlling quality, safety and efficacy of a pharmaceutical at each stage during drug development. An assay is the quantitative measurement of the active pharmaceutical ingredient in a substance, while purity refers to the assessment of the presence and level of impurities, involving qualitative or quantitative analysis. […]
Read MoreLearn about Chiral HPLC, a specialised technique for separating chiral compounds in pharmaceutical analysis. Understand its importance, applications, and how it works.
Read MoreLearn about climatic zones for stability studies, including their definition, types (ICH Zones I–IV), and importance in pharmaceutical and product development for global compliance and shelf-life testing.
Read MoreChiral chromatography is a specialized separation technique used to resolve enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—by employing a chiral stationary phase along with a liquid or gas mobile phase. This is where chiral chromatography becomes essential: it is a powerful analytical and preparative tool for distinguishing, separating, and studying these mirror-image compounds. Understanding […]
Read MoreValidation of pharmacopoeial methods should be performed using minimal analytical parameters, with a primary focus on specificity, detection limit, and quantification limit. Pharmacopoeial methods are presumed to be validated and therefore only require verification or partial validation. What is a Pharmacopoeial Method? Pharmacopoeial methods are analytical procedures published in recognised pharmacopoeias like: These methods are […]
Read MoreLearn key differences between Validation protocol and report with frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you better understand and implement them.
Read MoreThe signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio in HPLC is a key measure of analytical sensitivity. It is typically calculated using the formula: S/N = 2H/h. where H is the peak height and h is the noise height. In this blog post, I will discuss the concept of signal-to-noise ratio, how it’s determined, its role in establishing Detection […]
Read MoreChiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC) is a powerful separation technique used to resolve enantiomers—molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other—based on their differential interactions with a chiral stationary phase. Because different enantiomers of a compound can exhibit distinct biological activities, separating and controlling unwanted isomers is critical in the development of Active Pharmaceutical […]
Read MoreDiscover Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) – a fast, eco-friendly technique for separating complex mixtures. Learn its principles, pharmaceutical applications, advantages, limitations, and how it compares to HPLC and GC.
Read MoreLearn how Ion Exchange Chromatography is used in pharmaceutical analysis for precise quantification of cations and anions in APIs. Includes principles, procedures, case studies, and regulatory insights.
Read MoreExplore how DSC aids drug development by analyzing thermal behavior, stability, and polymorphism
Read Moreearn how to quantify polymorphic impurities in APIs using X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) with a step-by-step analytical approach, calibration formula, and a real-world Carbamazepine case study
Read MoreLearn what cross-validation of an analytical method is, why it’s important, when to perform it, and how it's done. Ensure method reliability, regulatory compliance, and data integrity across labs.
Read MoreLearn what polymorphism is in pharmaceuticals, its types, real-world examples, testing methods, regulatory guidelines, and its impact on drug development, stability, and bioavailability
Read MoreEssential HPLC equations and terminology encompass key parameters related to column separation, mobile and stationary phases, flow rate, retention time, and resolution. A clear understanding of these concepts is vital for accurate method development, optimisation, and reliable HPLC analysis. In this blog, I will discuss the fundamental HPLC terms and formulas that every chromatographer should […]
Read MoreLearn what analytical method revalidation is, when and how to perform it, and why it’s essential for ensuring accurate, compliant, and reliable lab results in regulated industries
Read MoreDiscover the key differences between methanol and acetonitrile in HPLC. Compare safety, cost, UV cut-off, resolution, peak shape, and more to determine the best solvent for your analysis.
Read MoreLearn what extractables and leachables are, how they differ, and how they are tested in the pharmaceutical industry.
Read MoreHPLC Column Washing by Sonication is used to remove strongly adsorbed materials and improve column performance HPLC columns can be cleaned effectively using sonication, a process that uses ultrasound waves to help remove built-up contaminants. This method is especially helpful for getting rid of strongly adsorbed substances that regular flushing might miss. To clean the […]
Read MoreExplore the difference between Ruggedness and Robustness testing in pharmaceutical analysis. Learn their importance in ensuring method reliability, consistency, and quality control across varying conditions
Read More
earn the key differences between analytical method development and validation using chromatographic, titrimetric, and mass spectrometric methods with case studies and FAQs.
Read MoreIntermediate precision measures variability within the same laboratory under different conditions (e.g., different days, analysts, instruments), while reproducibility measures variability between different laboratories, assessing method performance across different locations and setups. In the world of analytical chemistry and pharmaceutical quality control, method validation is critical to ensure that data generated from analytical tests is reliable, […]
Read MoreHPLC Mobile phase modifiers—such as trifluoroacetic acid and triethylamine—are chemical additives incorporated into the mobile phase to enhance peak efficiency, resolution, elution profiles, and selectivity in HPLC separations High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a cornerstone technique in analytical chemistry for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a mixture. One of the most critical aspects of […]
Read MoreLearn why degassing the mobile phase is essential in HPLC. Discover its impact on system performance, accuracy, and the best degassing methods used in modern labs."</strong></p> <!-- /wp:paragraph -->
Read MoreTechnology Transfer of Analytical Methods in Pharmaceuticals refers to the systematic process of transferring validated analytical methods from one laboratory (e.g., R&D, method development lab) to another (e.g., quality control, manufacturing site lab), ensuring the method performs equivalently and reliably at the receiving site. Analytical Method Transfer Analytical Method Transfer, also known as Technology Transfer […]
Read MoreBoth Chromatographic and Titrimetric methods are widely used in pharmaceutical analysis. The main difference between chromatographic and titrimetric methods is that the chromatographic method is selective, while the titrimetric method is not. Each has its strengths, limitations, and ideal applications. In this blog, we’ll discuss the differences between these two approaches, helping you understand when […]
Read MoreGC troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving common problems that can affect peak shape, retention time, resolution, sensitivity, and reproducibility GC systems can experience performance issues that affect accuracy, precision, and efficiency. In this article, I will discuss quick identification and resolution of these problems to ensure reliable results and minimise downtime GC Troubleshooting The process […]
Read MoreGC bleeding, also known as GC column bleed, occurs when the stationary phase thermally degrades at temperatures near the column’s upper limit, leading to unwanted baseline noise or artefacts. GC bleeding can reduce the quality, damage the detectors, and increase the analysis costs. In this post, we’ll break down what GC bleeding is, why it […]
Read More
Reverse Phase and Normal Phase HPLC are widely used in pharmaceutical development, still Reverse-Phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) is preferred over Normal-Phase HPLC (NP-HPLC) due to its better compatibility, broader analyte range, simpler method development, and easier system stabilisation. Reverse Phase And Normal Phase HPLC: Why Reverse Phase Is More Common? The following 6 main key reasons explain […]
Read MoreLearn causes peak tailing and fronting in HPLC, and procedure to reduce them with FAQs
Read MorePharmaceutical analysis is a significant contributor to the overall cost of drug development and manufacturing. For companies striving to stay competitive while adhering to stringent regulatory requirements, the challenge is clear: how do you reduce the cost of pharmaceutical analysis without compromising quality? Pharmaceutical Analysis: Tips to Reduce Cost Without Compromising Quality Pharmaceutical analysis plays […]
Read More
In Iodometric Titration, starch gives a water-insoluble complex with iodine. This water-insoluble complex creates problems in detecting the actual endpoint. This means that the endpoint appears before the actual endpoint. That is why the starch indicator is added just before the end point when the colour is pale-straw yellow. In analytical chemistry, iodometric titration stands […]
Read MoreLearn how to select, store, and handle HPLC-grade water to improve chromatographic performance. Discover best practices that ensure cleaner baselines, longer column life, and more reliable HPLC results.
Read MoreLearn to reduce HPLC method development cost in 12 easy steps.
Read MoreHPLC troubleshooting is the process of identifying common HPLC problems, their possible causes, and providing practical solutions to these problems to ensure reliable results and minimise downtime. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical technique used widely in pharmaceutical development and several other industries. However, like any complex instrument, HPLC systems can experience performance […]
Read MoreGC capillary columns are widely used in industries than packed columns because capillary columns give sharper peaks with less tailing, higher theoretical plates than packed columns Gas Chromatography (GC) is an analyticaln technique for separating volatile compounds in a mixture. A fundamental and vital component of GC systems is the column, and choosing between capillary […]
Read MorePolarimeter A polarimeter is an analytical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of an optically active substance. Optically Active Substance A substance is optically active if it can rotate the plane of polarised light. It is of two types: Dextrorotatory and Levorotatory Optical Activity depends upon the Molecular structure (presence of chiral centres), Wavelength, temperature and solvent […]
Read MoreLearn why filtering the mobile phase in HPLC is essential for accurate results, protecting your column, and ensuring system reliability. Discover best practices and FAQs.
Read MoreLearn difference between Iodometric and Iodimetric titration with case studies and FAQs
Read More
Learn titration, its types, method development steps with expert tips, case studies and FAQs
Read MoreQualitative and Quantitative Analysis: Qualitative analysis is used to identify the compound, whereas Quantitative analysis is used to determine the exact quantity /concentration of the compound. Qualitative And Quantitative Analysis Pharmaceutical analysis is broadly classified into two main categories: When a test is performed to identify a pharmaceutical substance or assess its purity (with or […]
Read MoreChiral Purity quantifies the proportion of one enantiomer in a mixture, with higher chiral purity indicating a greater concentration of the desired isomer. In pharmacology, for example, one enantiomer of a drug may be therapeutic, while the other could be harmful or inactive. Therefore, determining the chiral purity is critical to ensure the correct enantiomer […]
Read MoreLearn Potentiometric Titration and difference Between Potentiometric titration and Indicator type titration with case study
Read MoreReporting Results of Pharmaceutical Impurities: A Case Study
Read MoreLearn Modes Of Calculation In Chromatographic Analysis with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn how to set up Identification test specifications for pharmaceuticals
Read MoreLearn what enantiomeric excess is, how it's calculated, and its real-world applications with case studies.
Read More
Learn difference between Achiral and Chiral Molecules with examples and FAQs
Read More
Learn HPLC method development for basic molecules with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreHPLC Method Development For Acidic Molecules: A Case Study
Read MoreHPLC Method for Nonpolar Molecules; How to Separate Naphthalene and Anthracene?
Read More
Explore Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) in the pharmaceutical industry', its process, benefits, CA vs. PA, key elements, case studies, and its role in continuous improvement
Read More
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Read More
HPLC column, working principles, types, expert tips for optimal use, and effective cleaning and regeneration procedure
Read MoreLearn how to prepare and optimise HPLC mobile phases correctly with expert tips, cost-saving strategies, and real case studies
Read MoreDerivatisation in GC/GC-MS is essential for converting non-volatile or highly polar pharmaceuticals into volatile, stable, and analytically compatible derivatives suitable for chromatographic separation and detection.
Read MoreLearn HPLC method development from a chromatography expert with 30 years of experience. Includes practical tips, case studies, and FAQs
Read MoreLearn HPLC detector, types, selection procedure, expert tips with case study studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn everything about GC column, including types, how to select the right one, real-world case studies, and answers to frequently asked questions
Read MoreLearn how the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) classifies drugs based on solubility and permeability to predict oral drug absorption, bioavailability, and guide formulation development
Read More
Learn about GCMS in drug development; its principles, applications in industries, real-world case studies, and answers to frequently asked questions
Read More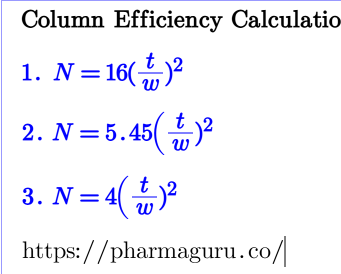
Learn about column efficiency in HPLC and GC, including its calculation, role in chromatographic methods, and acceptance criteria for optimal system performance
Read MoreIn HPLC, void volume refers to the volume within the column that is not occupied by stationary phase particles but is instead filled with the mobile phase. Dwell volume (also known as gradient delay volume and denoted as Vᴅ) is the volume of mobile phase between the solvent mixing point and the column inlet in […]
Read MoreLearn what resolution in HPLC means, how it’s calculated, key factors affecting it, and its role in method development and system suitability testing
Read More
Explore Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS) in pharmaceutical development - learn structure elucidation, ionisation modes, mass analyser, and expert tips with real-world case studies
Read MoreUnderstand the role of capacity factor in HPLC, including how to calculate it, why it matters in method development, and what affects its value for optimal chromatographic results
Read MoreLearn the importance of System Suitability Testing (SST) in chromatography for HPLC, GC, LCMS, and more. Discover how to establish SST criteria, evaluate system performance, and avoid common pitfalls during method development.
Read MoreThere is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Read More
Learn about HETP (Height equivalent to a theoretical plate). Explore its definition, calculation formula, influencing factors, applications, and real-world case studies to optimize column efficiency
Read MoreLearn the importance of photostability testing in pharmaceuticals, including procedures, benefits, case studies, and how it ensures drug safety, quality, and efficacy
Read MoreDiscover the importance of forced degradation studies in pharmaceutical development, including procedures, condition selection, impurity identification, and analytical strategies
Read MoreUnderstand the importance of Detection Limit (DL) and Quantification Limit (QL) in analytical method validation. Learn definitions, regulatory guidelines, and how to determine DL and QL in pharmaceutical analysis.
Read MoreLearn how to evaluate linearity and range in method validation with step-by-step procedures, a real-life case study, and answers to common FAQs. Gain the confidence to perform the test independently.
Read MoreExplore the importance of robustness in analytical method validation with practical guidance, a case study, and FAQs to help you perform the test effectively and efficiently
Read MoreLearn the importance of solution stability in analytical method validation with a practical case study. Understand why and how this test is performed, and gain the skills to apply it independently
Read MoreLearn Recovery Calculation In Analytical Method Validation with a step-by-step guide, real case study, and answers to common FAQs. Essential for accurate and reliable method development
Read MoreAccuracy in Analytical Method Validation is one of the most critical parameters, directly impacting the reliability and credibility of test results. It ensures that the method measures exactly what it is intended to, without bias or error. In this article, we will explore how to perform accuracy testing in analytical method validation, supported by step-by-step […]
Read More
Learn the complete procedure for evaluating precision in method validation, including system precision, method precision, reproducibility, and intermediate precision with real-world case studies
Read MoreLearn how to evaluate specificity during analytical method validation in pharmaceutical analysis. Includes step-by-step procedures, acceptance criteria, case study, and FAQs.
Read More
Learn Analytical Method Validation (AMV) step by step with clear guidelines, key parameters, classifications, and expert strategies. A must-read for pharma QA/QC professionals
Read More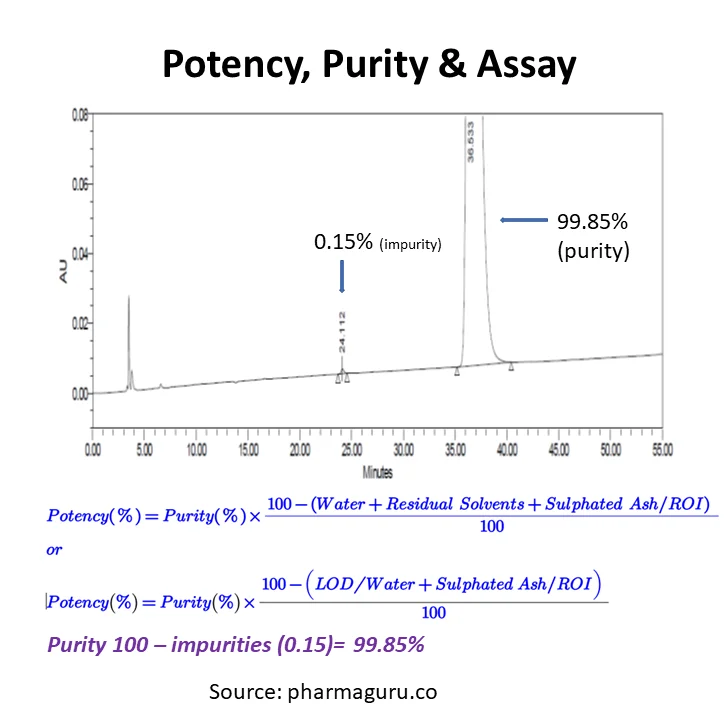
Understand potency, purity, and assay in pharma testing. Discover key differences, how to calculate them, and why they matter in drug development
Read More
Explore expert insights on nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals, including their toxicity, formation during manufacturing, detection challenges, and effective control strategies. Learn through case studies and FAQs
Read More
The Relative Response Factor (RRF) is defined as the ratio between the Response Factor of the impurity and the Response Factor of the main analyte standard. In pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring the quality and purity of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) is of paramount importance. This quality is often determined by analysing the impurity profile, which requires […]
Read MoreLearn the key differences between Analytical Method Validation and Verification in pharmaceutical analysis. Explore their applications, advantages, and case studies to gain practical insights into these essential processes
Read MoreExplore effective control of impurities in pharmaceuticals, covering sources, types, challenges, and regulatory guidelines. Learn advanced analytical techniques and real-world case studies to enhance drug quality, safety, and efficacy
Read MoreDiscover various methods to determine pKa values, including titration, UV-Vis spectroscopy, NMR, HPLC, and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Learn the principles, procedures, and applications of each technique for accurate pKa determination.
Read MoreExplore the importance of solubility in drug development, bioequivalence, and quality control. Learn about solubility principles, classification, calculation by HPLC, and factors affecting solubility. Dive into pharmaceutical solvent selection, case studies, and FAQs to enhance your understanding."
Read More
This article describes Genotoxicity and Mutagenicity, chemistry behind genotoxicity and mutagenicity and structure alert concept to identifying genotoxins
Read More
The chromatographic peaks that do not belong to the sample matrix or diluent and whose origin is unknown are called ghost peaks.
Read More
This article describes equivalent HPLC columns, steps for selection of equivalent column with case studies and FAQs
Read More
The specified and unspecified Impurities play a vital role in the related substance or impurities profile specification of any pharmaceutical. Both specified and unspecified Impurities refer to the identification, control, and regulation of these impurities during drug development and manufacturing.
Read More
HPTLC is a modified and advanced version of the TLC technique. It is a powerful analytical technique that provides a highly sensitive, reproducible, and cost-effective means of separating, identifying, and quantifying components in a mixture.
Read MoreICPMS is an advanced analytical technique widely used in pharmaceutical development for detecting trace metals, including both essential and potentially harmful elements, at very low concentrations. Its high sensitivity and precision make it invaluable in a range of applications, from raw material testing to quality control of final APIs (Active pharmaceutical ingredients).
Read MoreQuick Links