Learn key differences between Validation protocol and report with frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you better understand and implement them.
Read MoreThe signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio in HPLC is a key measure of analytical sensitivity. It is typically calculated using the formula: S/N = 2H/h. where H is the peak height and h is the noise height. In this blog post, I will discuss the concept of signal-to-noise ratio, how it’s determined, its role in establishing Detection […]
Read MoreHow to Read a Chromatogram is one of the fundamental skills to proceed with the HPLC and GC analysis. A chromatogram is interpreted by analysing the axes, identifying the peaks, and evaluating their characteristics such as Retention Time, Peak Shape, Peak Height and Area. In this article, I will explain how to read and interpret […]
Read MoreChiral GC (Gas Chromatography) is a separation technique used to separate enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—based on their interaction with a chiral stationary phase. This method is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, where different enantiomers of a compound can have distinct biological effects, ensuring precise analysis and quality control. It is a […]
Read MoreDiscover Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) – a fast, eco-friendly technique for separating complex mixtures. Learn its principles, pharmaceutical applications, advantages, limitations, and how it compares to HPLC and GC.
Read MoreLearn how Ion Exchange Chromatography is used in pharmaceutical analysis for precise quantification of cations and anions in APIs. Includes principles, procedures, case studies, and regulatory insights.
Read MoreExplore how DSC aids drug development by analyzing thermal behavior, stability, and polymorphism
Read Moreearn how to quantify polymorphic impurities in APIs using X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) with a step-by-step analytical approach, calibration formula, and a real-world Carbamazepine case study
Read MoreLearn what cross-validation of an analytical method is, why it’s important, when to perform it, and how it's done. Ensure method reliability, regulatory compliance, and data integrity across labs.
Read MoreLearn what polymorphism is in pharmaceuticals, its types, real-world examples, testing methods, regulatory guidelines, and its impact on drug development, stability, and bioavailability
Read MoreEssential HPLC equations and terminology encompass key parameters related to column separation, mobile and stationary phases, flow rate, retention time, and resolution. A clear understanding of these concepts is vital for accurate method development, optimization, and reliable HPLC analysis. In this blog, I will discuss the fundamental HPLC terms and formulas that every chromatographer should […]
Read MoreLearn what analytical method revalidation is, when and how to perform it, and why it’s essential for ensuring accurate, compliant, and reliable lab results in regulated industries
Read MoreLearn how to choose between HPLC and GC for related substances testing in pharmaceuticals. Compare compatibility, volatility, cost, accuracy, and regulatory compliance.
Read MoreDiscover the key differences between methanol and acetonitrile in HPLC. Compare safety, cost, UV cut-off, resolution, peak shape, and more to determine the best solvent for your analysis.
Read MoreLearn what extractables and leachables are, how they differ, and how they are tested in the pharmaceutical industry.
Read MoreHPLC Column Washing by Sonication is used to remove strongly adsorbed materials and improve column performance HPLC columns can be cleaned effectively using sonication, a process that uses ultrasound waves to help remove built-up contaminants. This method is especially helpful for getting rid of strongly adsorbed substances that regular flushing might miss. To clean the […]
Read MoreAnalytical Method Development and Validation: Method Development involves designing a reliable technique to identify and quantify chemical substances, while Analytical Method Validation confirms that this developed method consistently delivers accurate, precise, and reproducible results for its intended purpose. In the world of pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and chemical manufacturing, analytical methods are essential tools for ensuring the […]
Read MoreIntermediate precision measures variability within the same laboratory under different conditions (e.g., different days, analysts, instruments), while reproducibility measures variability between different laboratories, assessing method performance across different locations and setups. In the world of analytical chemistry and pharmaceutical quality control, method validation is critical to ensure that data generated from analytical tests is reliable, […]
Read MoreHPLC Mobile phase modifiers—such as trifluoroacetic acid and triethylamine—are chemical additives incorporated into the mobile phase to enhance peak efficiency, resolution, elution profiles, and selectivity in HPLC separations High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a cornerstone technique in analytical chemistry for separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in a mixture. One of the most critical aspects of […]
Read MoreLearn why degassing the mobile phase is essential in HPLC. Discover its impact on system performance, accuracy, and the best degassing methods used in modern labs."</strong></p> <!-- /wp:paragraph -->
Read MoreTechnology Transfer of Analytical Methods in Pharmaceuticals refers to the systematic process of transferring validated analytical methods from one laboratory (e.g., R&D, method development lab) to another (e.g., quality control, manufacturing site lab), ensuring the method performs equivalently and reliably at the receiving site. Analytical Method Transfer Analytical Method Transfer, also known as Technology Transfer […]
Read MoreBoth Chromatographic and Titrimetric methods are widely used in pharmaceutical analysis. The main difference between chromatographic and titrimetric methods is that the chromatographic method is selective, while the titrimetric method is not. Each has its strengths, limitations, and ideal applications. In this blog, we’ll discuss the differences between these two approaches, helping you understand when […]
Read MoreGC troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving common problems that can affect peak shape, retention time, resolution, sensitivity, and reproducibility GC is a powerful analytical technique used widely in pharmaceutical development and several other industries. However, like any complex instrument, GC systems can experience performance issues that affect accuracy, precision, and efficiency. In this article, I […]
Read MoreGC bleeding, also known as GC column bleed, occurs when the stationary phase thermally degrades at temperatures near the column’s upper limit, leading to unwanted baseline noise or artefacts. GC bleeding can reduce the quality, damage the detectors, and increase the analysis costs. In this post, we’ll break down what GC bleeding is, why it […]
Read More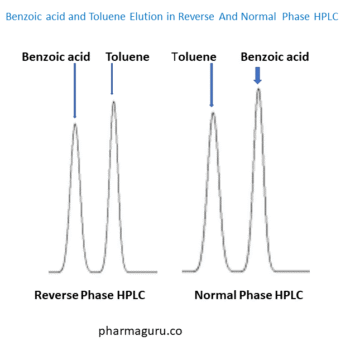
Reverse Phase And Normal Phase HPLC are widely used in pharmaceutical development, still Reverse-Phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) is preferred over Normal-Phase HPLC (NP-HPLC) due to its better compatibility, broader analyte range, simpler method development, and easier system stabilisation. Reverse Phase And Normal Phase HPLC: Why Reverse Phase Is More Common The following 6 main key reasons explain […]
Read MoreLearn causes peak tailing and fronting in HPLC, and procedure to reduce them with FAQs
Read MorePharmaceutical analysis is a significant contributor to the overall cost of drug development and manufacturing. For companies striving to stay competitive while adhering to stringent regulatory requirements, the challenge is clear: how do you reduce the cost of pharmaceutical analysis without compromising quality? Pharmaceutical Analysis: Tips to Reduce Cost Without Compromising Quality Pharmaceutical analysis plays […]
Read MoreIn Iodometric Titration, starch gives a water-insoluble complex with iodine. This water-insoluble complex creates problems in detecting the actual endpoint. This means that the endpoint appears before the actual endpoint. That is why the starch indicator is added just before the end point when the colour is pale-straw yellow. In analytical chemistry, iodometric titration stands […]
Read MoreLearn how to select, store, and handle HPLC-grade water to improve chromatographic performance. Discover best practices that ensure cleaner baselines, longer column life, and more reliable HPLC results.
Read MoreHow to Reduce HPLC Method Development Cost: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is the most widely used and essential technique in pharmaceutical development. However, the process of developing and validating a robust HPLC method can be time-consuming and expensive. Fortunately, there are effective ways to streamline your method development while keeping costs under control, without sacrificing […]
Read MoreHPLC troubleshooting is the process of identifying common HPLC problems, their possible causes, and providing practical solutions to these problems to ensure reliable results and minimise downtime. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical technique used widely in pharmaceutical development and several other industries. However, like any complex instrument, HPLC systems can experience performance […]
Read MoreGC capillary columns are widely used in industries than packed columns because capillary columns give sharper peaks with less tailing, higher theoretical plates than packed columns Gas Chromatography (GC) is an analyticaln technique for separating volatile compounds in a mixture. A fundamental and vital component of GC systems is the column, and choosing between capillary […]
Read MorePolarimeter A polarimeter is an analytical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of an optically active substance. Optically Active Substance A substance is optically active if it can rotate the plane of polarised light. It is of two types: Dextrorotatory and Levorotatory Optical Activity depends upon the Molecular structure (presence of chiral centres), Wavelength, […]
Read MoreLearn Reverse Phase HPLC and Normal Phase HPLC, key differences, including their principles, applications, advantages, and FAQs
Read MoreLearn why filtering the mobile phase in HPLC is essential for accurate results, protecting your column, and ensuring system reliability. Discover best practices and FAQs.
Read MoreLearn difference between Iodometric and Iodimetric titration with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn thin-layer chromatography, its principle, method development steps, expert tips with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn titration, its types, method development steps with expert tips, case studies and FAQs
Read MoreQualitative and Quantitative Analysis: Qualitative analysis is used to identify the compound, whereas Quantitative analysis is used to determine the exact quantity /concentration of the compound. Qualitative And Quantitative Analysis Pharmaceutical analysis is broadly classified into two main categories: When a test is performed to identify a pharmaceutical substance or assess its purity (with or […]
Read MoreChiral Purity quantifies the proportion of one enantiomer in a mixture, with higher chiral purity indicating a greater concentration of the desired isomer. In pharmacology, for example, one enantiomer of a drug may be therapeutic, while the other could be harmful or inactive. Therefore, determining the chiral purity is critical to ensure the correct enantiomer […]
Read MoreLearn Potentiometric Titration and difference Between Potentiometric titration and Indicator type titration with case study
Read MoreReporting Results of Pharmaceutical Impurities: A Case Study
Read MoreLearn Modes Of Calculation In Chromatographic Analysis with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn how to set up Identification test specifications for pharmaceuticals
Read MoreLearn what enantiomeric excess is, how it's calculated, and its real-world applications with case studies.
Read More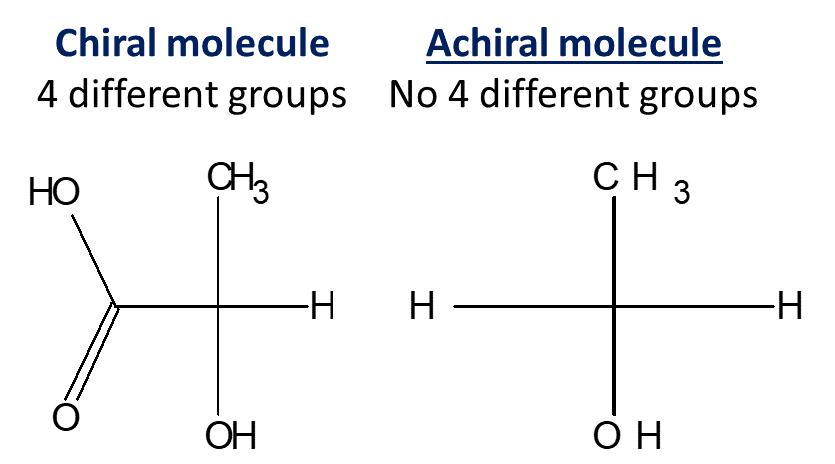
Learn difference between Achiral and Chiral Molecules with examples and FAQs
Read MoreLearn HPLC method development for basic molecules with case studies and FAQs
Read MoreHPLC Method Development For Acidic Molecules: A Case Study
Read MoreHPLC Method for Nonpolar Molecules; How to Separate Naphthalene and Anthracene?
Read More
Explore Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) in the pharmaceutical industry', its process, benefits, CA vs. PA, key elements, case studies, and its role in continuous improvement
Read MoreLearn GC method development step by step with case studies, expert tips and FAQs
Read MoreHPLC column, working principles, types, expert tips for optimal use, and effective cleaning and regeneration procedure
Read MoreLearn how to prepare and optimise HPLC mobile phases correctly with expert tips, cost-saving strategies, and real case studies
Read MoreAnalysing non-volatile compounds with GC using Derivatisation
Read MoreLearn HPLC method development from a chromatography expert with 30 years of experience. Includes practical tips, case studies, and FAQs
Read MoreLearn HPLC detector, types, selection procedure, expert tips with case study studies and FAQs
Read MoreLearn everything about GC column, including types, how to select the right one, real-world case studies, and answers to frequently asked questions
Read MoreLearn how the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) classifies drugs based on solubility and permeability to predict oral drug absorption, bioavailability, and guide formulation development
Read MoreLearn about column efficiency in HPLC and GC, including its calculation, role in chromatographic methods, and acceptance criteria for optimal system performance
Read MoreIn HPLC, void volume refers to the volume within the column that is not occupied by stationary phase particles but is instead filled with the mobile phase. Dwell volume (also known as gradient delay volume and denoted as Vᴅ) is the volume of mobile phase between the solvent mixing point and the column inlet in […]
Read MoreLearn what resolution in HPLC means, how it’s calculated, key factors affecting it, and its role in method development and system suitability testing
Read MoreExplore Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS) in pharmaceutical development - learn structure elucidation, ionisation modes, mass analyser, and expert tips with real-world case studies
Read MoreUnderstand the role of capacity factor in HPLC, including how to calculate it, why it matters in method development, and what affects its value for optimal chromatographic results
Read MoreLearn the importance of System Suitability Testing (SST) in chromatography for HPLC, GC, LCMS, and more. Discover how to establish SST criteria, evaluate system performance, and avoid common pitfalls during method development.
Read MoreLearn about the tailing factor in HPLC and GC, including its calculation, significance in method development, acceptance criteria, and key factors affecting peak symmetry in chromatographic analysis.
Read MoreLearn about HETP (Height equivalent to a theoretical plate). Explore its definition, calculation formula, influencing factors, applications, and real-world case studies to optimize column efficiency
Read MoreLearn the importance of photostability testing in pharmaceuticals, including procedures, benefits, case studies, and how it ensures drug safety, quality, and efficacy
Read MoreDiscover the importance of forced degradation studies in pharmaceutical development, including procedures, condition selection, impurity identification, and analytical strategies
Read MoreUnderstand the importance of Detection Limit (DL) and Quantification Limit (QL) in analytical method validation. Learn definitions, regulatory guidelines, and how to determine DL and QL in pharmaceutical analysis.
Read MoreLearn how to evaluate linearity and range in method validation with step-by-step procedures, a real-life case study, and answers to common FAQs. Gain the confidence to perform the test independently.
Read MoreExplore the importance of robustness in analytical method validation with practical guidance, a case study, and FAQs to help you perform the test effectively and efficiently
Read MoreLearn the importance of solution stability in analytical method validation with a practical case study. Understand why and how this test is performed, and gain the skills to apply it independently
Read MoreLearn Recovery Calculation In Analytical Method Validation with a step-by-step guide, real case study, and answers to common FAQs. Essential for accurate and reliable method development
Read MoreAccuracy in Analytical Method Validation is one of the most critical parameters, directly impacting the reliability and credibility of test results. It ensures that the method measures exactly what it is intended to, without bias or error. In this article, we will explore how to perform accuracy testing in analytical method validation, supported by step-by-step […]
Read More
Learn the complete procedure for evaluating precision in method validation, including system precision, method precision, reproducibility, and intermediate precision with real-world case studies
Read MoreLearn how to evaluate specificity during analytical method validation in pharmaceutical analysis. Includes step-by-step procedures, acceptance criteria, case study, and FAQs.
Read More
Learn Analytical Method Validation (AMV) step by step with clear guidelines, key parameters, classifications, and expert strategies. A must-read for pharma QA/QC professionals
Read More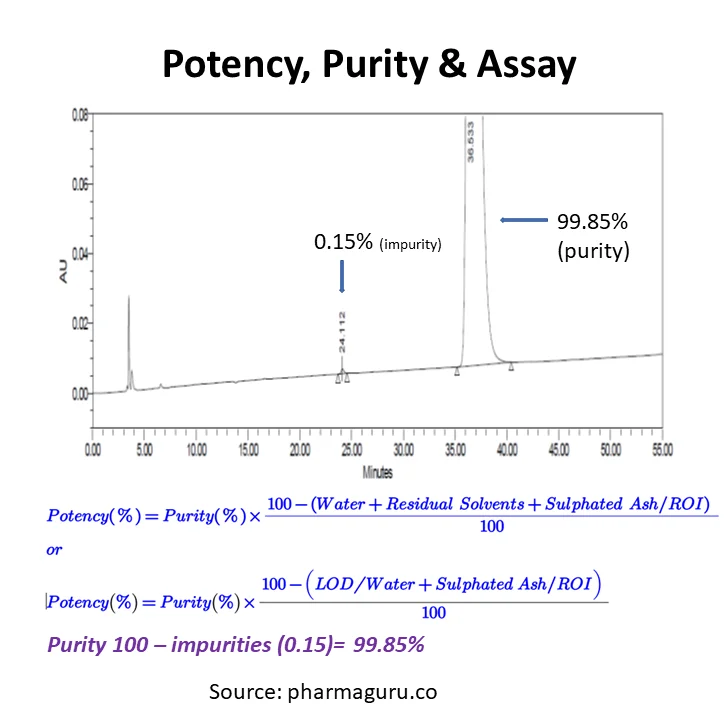
Understand potency, purity, and assay in pharma testing. Discover key differences, how to calculate them, and why they matter in drug development
Read MoreExplore expert insights on nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals, including their toxicity, formation during manufacturing, detection challenges, and effective control strategies. Learn through case studies and FAQs
Read More
The Relative Response Factor (RRF) is defined as the ratio between the Response Factor of the impurity and the Response Factor of the main analyte standard. In pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring the quality and purity of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) is of paramount importance. This quality is often determined by analysing the impurity profile, which requires […]
Read MoreLearn the key differences between Analytical Method Validation and Verification in pharmaceutical analysis. Explore their applications, advantages, and case studies to gain practical insights into these essential processes
Read MoreExplore effective control of impurities in pharmaceuticals, covering sources, types, challenges, and regulatory guidelines. Learn advanced analytical techniques and real-world case studies to enhance drug quality, safety, and efficacy
Read MoreDiscover various methods to determine pKa values, including titration, UV-Vis spectroscopy, NMR, HPLC, and the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Learn the principles, procedures, and applications of each technique for accurate pKa determination.
Read MoreExplore the importance of solubility in drug development, bioequivalence, and quality control. Learn about solubility principles, classification, calculation by HPLC, and factors affecting solubility. Dive into pharmaceutical solvent selection, case studies, and FAQs to enhance your understanding."
Read More
This article describes Genotoxicity and Mutagenicity, chemistry behind genotoxicity and mutagenicity and structure alert concept to identifying genotoxins
Read More
The chromatographic peaks that do not belong to the sample matrix or diluent and whose origin is unknown are called ghost peaks.
Read More
This article describes equivalent HPLC columns, steps for selection of equivalent column with case studies and FAQs
Read More
The specified and unspecified Impurities play a vital role in the related substance or impurities profile specification of any pharmaceutical. Both specified and unspecified Impurities refer to the identification, control, and regulation of these impurities during drug development and manufacturing.
Read More
HPTLC is a modified and advanced version of the TLC technique. It is a powerful analytical technique that provides a highly sensitive, reproducible, and cost-effective means of separating, identifying, and quantifying components in a mixture.
Read MoreICPMS is an advanced analytical technique widely used in pharmaceutical development for detecting trace metals, including both essential and potentially harmful elements, at very low concentrations. Its high sensitivity and precision make it invaluable in a range of applications, from raw material testing to quality control of final APIs (Active pharmaceutical ingredients).
Read MoreQuick Links