Chiral chromatography is a specialized separation technique used to resolve enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—by employing a chiral stationary phase along with a liquid or gas mobile phase. This is where chiral chromatography becomes essential: it is a powerful analytical and preparative tool for distinguishing, separating, and studying these mirror-image compounds. Understanding […]
Chiral chromatography is a specialized separation technique used to resolve enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—by employing a chiral stationary phase along with a liquid or gas mobile phase.
This is where chiral chromatography becomes essential: it is a powerful analytical and preparative tool for distinguishing, separating, and studying these mirror-image compounds. Understanding how this technique works and why it matters is fundamental in many scientific fields, especially in pharmaceuticals.
Chiral column chromatography plays a critical role in the separation of chiral pharmaceuticals. Because chiral drugs contain atoms arranged in specific three-dimensional orientations, each enantiomer can interact differently with biological systems. These differences can lead to variations in therapeutic activity, safety, and side-effect profiles. For this reason, ensuring the purity and proper characterisation of each enantiomer is vital in drug development.
However, the separation of chiral pharmaceuticals remains one of the more challenging tasks for chromatographers due to the subtle chemical differences between enantiomers.
In this article, I will share skill-based insights into the importance of chiral column chromatography in the pharmaceutical industry, the historical and scientific background of chirality—including the thalidomide tragedy—along with the distinction between chiral and achiral molecules. We will review the principles of chiral chemistry, explore major techniques used for chiral separation, examine various chiral stationary phases, and conclude with practical case studies and answers to frequently asked questions.
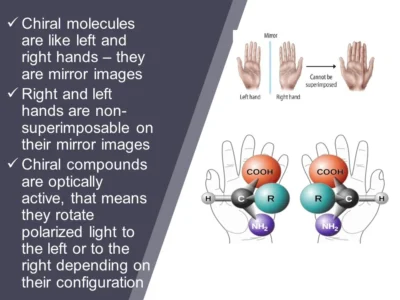
Chiral molecules are common in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and food additives. For example:
Chiral chromatography allows scientists to:
Chiral chromatography is a technique used to separate and analyse enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other but not superimposable. It uses a chiral stationary phase that interacts differently with each enantiomer, allowing them to be separated based on their distinct chemical behaviours. This method is widely used in pharmaceutical and chemical industries to ensure the purity and safety of chiral compounds.
The heart of chiral chromatography is the chiral stationary phase, which interacts differently with each enantiomer. Common CSPs include:
A notable example highlighting the importance of chiral separation in drug safety is the case of thalidomide. In the 1960s, thalidomide was used as a sedative and anti-nausea medication for pregnant women. However, it was later discovered that one enantiomer of thalidomide caused severe birth defects, while the other enantiomer was therapeutically active. Its R-form is biologically active, whereas the S-form is Teratogenic in nature.
This tragic event emphasised the importance of analysing and separating enantiomers to ensure the safety of pharmaceutical compounds. Since then, regulatory authorities have implemented strict guidelines requiring the evaluation of chiral purity for new drug candidates.
Chiral chromatography plays a crucial role in modern science and industry. As the demand for enantiomerically pure substances increases, especially in drug development, this technique continues to evolve with more efficient columns and faster separations.
Related:
Chiral purity refers to the presence of a single enantiomer in a pharmaceutical compound. It is crucial to ensure that drugs contain the desired enantiomer in the desired quantity to achieve the desired therapeutic effect and minimise potential side effects.
A2: Yes, chiral separation can potentially improve the efficacy of existing drugs by isolating the active enantiomer and eliminating the inactive or less effective enantiomer.
Yes, regulatory authorities, such as the FDA, require the evaluation of chiral purity for new drug candidates to ensure their safety and efficacy.
A4: Chiral separation can be challenging due to the similarity in physical and chemical properties of enantiomers. It requires the use of specialised techniques and careful optimisation to achieve efficient and selective separation.
Yes, chiral separation techniques can be applied to various industries, including agrochemicals, flavors and fragrances, and the food industry, to separate and analyze chiral compounds.
Chiral chromatography is a technique used to separate and analyse enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other but not superimposable. It uses a chiral stationary phase that interacts differently with each enantiomer, allowing them to be separated based on their distinct chemical behaviours. This method is widely used in pharmaceutical and chemical industries to ensure the purity and safety of chiral compounds.
The principle of chiral separation is based on the different interactions between enantiomers (mirror-image molecules) and a chiral stationary phase. Since enantiomers have identical physical and chemical properties except for their spatial arrangement, the chiral stationary phase can differentiate them by selectively binding to one enantiomer more strongly than the other. This differential interaction causes the enantiomers to travel at different rates through the chromatographic system, leading to their separation
The advantages of chiral chromatography include:
Further Reading
Quick Links