Learn the key differences between Analytical Method Validation and Verification in pharmaceutical analysis. Explore their applications, advantages, and case studies to gain practical insights into these essential processes
Both Validation and Verification are conducted to assess the suitability of an analytical method for its intended use. However, the key difference lies in their scope: method validation involves a comprehensive evaluation of all relevant parameters, while method verification focuses only on a select few, typically to confirm the method’s performance under specific conditions
In the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and consistency of analytical methods is critical for product quality, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. Two essential processes – Analytical Method Validation and Analytical Method Verification – play pivotal roles in achieving these objectives. However, due to limitations such as time, cost, and resources, not every pharmaceutical company can afford to conduct a full method validation for each analytical procedure. As a result, Analytical Method Verification is often utilised in specific scenarios.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Analytical Method Validation and Verification, exploring their differences, applications, advantages, and real-world case studies. By the end, readers will gain practical, skill-based knowledge on when and how to apply these processes effectively, as well as answers to FAQs (frequently asked questions) about this often misunderstood area of pharmaceutical analysis
Major Takeaway: FAQs On Analytical Method Verification
Analytical method validation confirms suitability of any method for its intended use.
Analytical method verification is performed to avoid any failure during complete validation.
In the verification few parameters like specificity, DL, QL, precision are performed. Validation parameters are selected based on the criticality of the method
Analytical method mini-validation can be performed for newly developed methods, for pharmacopeial methods and for customers’ method
The analytical project coordinator is responsible for Analytical method verification
The major difference is in Analytical validation, all parameters are performed, whereas in analytical method verification only a few parameters are performed.
It indicates the suitability of the method for the intended use. It is also accepted by regulatory agencies.
First, find out the criticality of the method. Based on criticality select validation parameters, perform the validation and make the report.
Analytical method verification is performed to check the suitability and validity of an Analytical method for its intended use. This test confirms that the method will pass the Analytical Method validation test if performed.
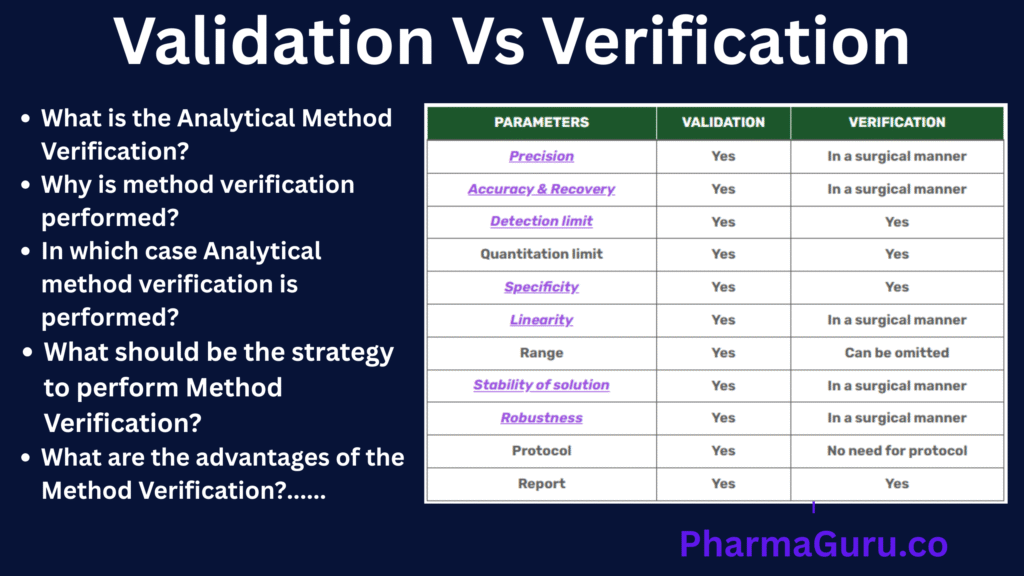
In Analytical validation, all parameters are performed as per the approved protocol. The major difference between Validation and Verification is that in Analytical validation, all parameters are performed, whereas in analytical method verification, only a few parameters are performed.
The following are the differences between Analytical Method Validation and Verification:
| Parameters | Validation | Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Yes | In a surgical manner |
| Accuracy & Recovery | Yes | In a surgical manner |
| Detection limit | Yes | Yes |
| Quantitation limit | Yes | Yes |
| Specificity | Yes | Yes |
| Linearity | Yes | In a surgical manner |
| Range | Yes | Can be omitted |
| Stability of solution | Yes | In a surgical manner |
| Robustness | Yes | In a surgical manner |
| Protocol | Yes | No need for protocol |
| Report | Yes | Yes |
This study is performed to check the suitability and validity of an Analytical method for its intended use. This test confirms that the method will pass the Analytical Method validation test if performed.
In the Analytical method verification, selected parameters of the Analytical validation are carried out surgically. Based on the sensitivity of the method project coordinator decides the Analytical method verification parameters.
Verification is performed in a G:P environment in the following cases:
1. For newly developed methods
Once any Analytical method is developed then verification is performed and a report is prepared. In this case, it is part of the development report.
Later on, complete Analytical method validation may be performed based on requirements.
2. For those methods which are used only to answer regulatory queries
When the method is developed to answer only regulatory queries, customer queries and deficiency letter queries to see the trend data and only for limited use (not for routine use), In that case, verification is performed.
In that case, there is no need for complete Analytical method validation.
3. Validated customer’s method
When any method is taken from the outside (e.g. customer) for analysis and release of the sample in that case verification is performed.
4. Methods which are validated in the commercial laboratory
If any method has been validated in the commercial laboratory, in that case, Analytical mini-validation is performed before batch analysis and release.
5. Pharmacopeial method
Sometimes the sample is analyzed and released by the Pharmacopeial method. Verification is performed for such methods to check the suitability of the method for the required analysis.
In the Pharmacopeial method generally, specificity, DL, QL precision and recovery are performed.
Verification is performed for both published and draft Pharmacopoeia methods.
Responsibility
Generally, the Analytical department is responsible for Analytical method verification. The project coordinator decides the analytical parameters for verification
Expert Tip: In Analytical method verification there is no need to prepare the protocol
The following are the advantages of verification or analytical method verification
Selection of verification parameters for separation of Benzene, Naphthalene and Anthracene in following HPLC chromatographic condition:
The following are the elution patterns of Benzene, Naphthalene and Anthracene in the above HPLC chromatographic conditions:

Selection of Verification parameters
Each peak is well separated from the adjacent peak, and secondly, each analyte (Benzene, Naphthalene and Anthracene) is non-polar. Thus, mobile phase composition will not have much effect on resolution. Therefore, one can consider specificity, DL (detection limit), QL (quantification limit) and precision in the verification test. You don’t need to do the robustness test.
Selection of verification parameters for separation of Ortho Cresol, Meta Cresol and Para Cresol: in the following HPLC chromatographic condition:
The following are the elution patterns of different analytes in the above HPLC chromatographic conditions:
Retention time:

Each peak is not well separated from the adjacent peak. There is no baseline separation between meta cresol and para cresol. Secondly, the separation is highly dependent on pH and therefore, in addition to specificity, DL (detection limit), QL (quantification limit) and precision, verification testing must consider pH variation.
Verification testing is performed for assay, impurity profile, content test, genotoxicity test, residual solvent tests, purity and chiral purity test using the following analytical techniques:
I hope this post has clarified the key differences between validation and verification in analytical methods. It’s essential to recognise that verification should always be conducted with the end goal in mind: ensuring that the method will meet the requirements of the full validation study. By aligning verification with the method’s ultimate purpose, you can optimise the process and enhance the likelihood of a successful validation.
Related:
Abbreviations
References
Quick Links