Discover the importance of forced degradation studies in pharmaceutical development, including procedures, condition selection, impurity identification, and analytical strategies
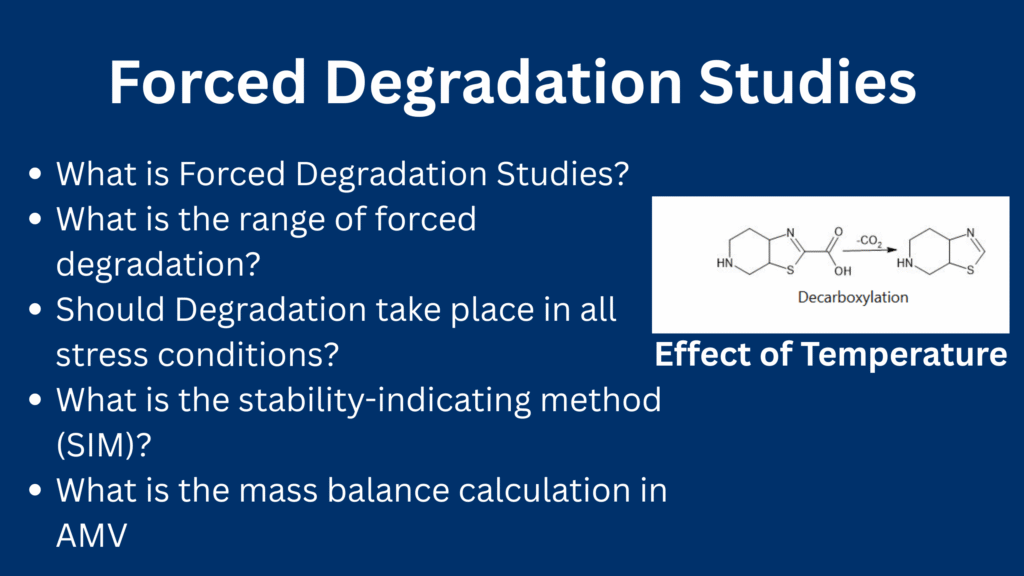
Forced degradation studies are scientifically designed experiments in which active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and finished products are subjected to extreme stress conditions-such as heat, light, humidity, acidic or basic environments, and oxidative agents-beyond those typically encountered during normal storage or use
These studies play a key role in drug development by helping to ensure the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Although these studies can be costly, time-consuming, and require a strong foundation in chemistry and analytical expertise, their value in understanding a drug’s stability profile is undeniable. Recognising this, I’ve decided to share my practical, skill-based insights to help others navigate this complex process.
In this article, you will learn about:
Major Takeaway: FAQS
ICH Q1A, QIB
Degradation of drug substances should be between 5% and 20%
Forced degradation is carried out under stressed conditions like temperature, acid and alkali hydrolysis, oxidation etc. Hence forced degradation and stress testing are the same.
Degradation of drug substances should be between 5% and 20%
Initially, forced degradation is calculated by area % or the area normalisation method
A validated analytical procedure that can be used to determine how the stability of drug substances and drug products changes over time is called the SIM or stability signal method. All degradation impurities must be separated in the method.
The solution of the compound is hydrolysed with 0.1N hydrochloric acid at room temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 30oC, 40oC, 50oC etc, if require.
5% and 20%
One representative sample is used for forced degradation studies
Forced degradation studies be performed above the accelerated test condition temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 40oC, 50oC, 60oC, 70oC, 80oC, 90oC, 100oC etc.
The solution of the compound is hydrolysed with 0.1N H2SO4 at room temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 30oC, 40oC, 50oC etc, if require.
Not necessary
LC-MS is used to identify degradation products forced degradation.
A SIM method is used for degradation products testing during forced degradation studies
The difference between assay and purity should be around 5%
No
% of Mass balance = Purity -Assay, where purity = (100 – total impurities)
Many impurities are generated during forced degradation of any AIP and result in reduced purity and assay. Mass balance gives the relationship between the purity of the degraded sample and the assay
The mass balance states that the amount of impurities formed during degradation must be equal to the loss of assay value of the degraded sample
Forced degradation studies are deliberate pharmaceutical studies in which drug substances (APIs) and finished products are exposed to extreme stress conditions such as heat, light, humidity, acid/base, and oxidation-beyond those encountered during normal storage or use. These studies are designed to accelerate chemical degradation, helping to identify potential degradation products, understand degradation pathways, and assess the intrinsic stability of the drug. The primary objective is to support the development of stability-indicating analytical methods (SIMs) and to enhance understanding of the drug’s behaviour under various stress conditions.
You may like:
The following are the main purposes of the forced degradation study:
Forced Degradations Strategy should be vision-based taking the help of brainstorming sessions of all concerned persons. The following are some important components:
An approved protocol should be used for the Forced Degradation study
The analytical method used in the Forced Degradation studies must be stability indicating (SIM)
Fully characterised primary standards or pharmacopeial standards with valid COA are used for Forced Degradation studies
Forced Degradation is performed on a single representative batch of the Active pharmaceutical ingredient and Drug product. Forced degradation is not performed on pharmaceutical raw material used in the synthesis of APIs and intermediates
Chemicals and reagents used in forced degradation must be as per the method and with valid COA
| FD Components | FD Conditions |
|---|---|
| Effect of temperature on solution or suspension | It should be performed above the accelerated test condition temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 40oC, 50oC, 60oC, 70oC, 80oC, 90oC, 100oC etc. |
| Oxidation (on solution or suspension) | The solution of the API or its products should be oxidised with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 30oC, 40oC, 50oC etc, if require |
| Hydrolysis (on solution or suspension) | Both acid and base hydrolysis should be performed across a wide range of pH. The solution of the compound should be hydrolysed with 0.1N hydrochloric acid or 0.1N sodium hydroxide at room temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 30oC, 40oC, 50oC etc, if require. |
| Humidity (on solid compound) | Humidity should be 80% RH or greater or as applicable for the API |
| Sunlight exposure (on solution or suspension) | The solution or suspension of the API or its products in a colourless transparent borosilicate glass vessel or quartz glass vessel should be placed in the SUNSET cabinet* or Xenon lamp |
| Effect of temperature on a solid sample | It should be performed above the accelerated test condition temperature. The temperature should be increased in 10-degree increments like 40oC, 50oC, 60oC, 70oC, 80oC etc. |
| Sunlight exposure (on solid sample) | Solid compound up to 3 mm layer spread in a borosilicate glass dish or quartz glass dish and the SUNSET cabinet or Xenon lamp (300 – 800 nm) for light exposure |
| Photostability |
Note:
Each degraded sample is tested or reviewed for the following parameters:
Degradation of drug substances between 5% and 20% is recommended. More degradation can lead to degradation of the degradation impurities ( secondary and tertiary degradation) and the same will not give any idea about the actual degradation product. That is why 5% and 20% is recommended is recommended.
The degradation does not need to take place in all stressed conditions. The condition in which degradation is not taking place can be terminated.
Many impurities can form during forced degradation studies. It may be possible that two or more impurities may co-elute or the impurity/impurities may merge with the main analyte peak.
Therefore, peak purity testing is required to determine the specificity or homogeneity of peaks. The PDA detector provides information about the homogeneity/purity of the peak.
Note: It is not applicable for degradation impurities that have a similar UV spectrum to the API.
A validated analytical procedure that can be used to determine how the stability of drug substances and drug products changes over time is called the SIM or stability signal method. A stability-indicating method accurately measures changes in the concentration of active ingredients without interference from other degradation products, impurities and excipients.
The stability indicating method which is used for Forced Degradation Studies, must be validated for precision, detection limit, quantification limit, accuracy, recovery, linearity, stability of solution and robustness. RRF of known degradation impurities should also be calculated. Actual known impurities should be isolated, and characterised, and potency should be calculated.
Impurities above the identification threshold (usually 0.1%) must be isolated, identified, characterized and potency should be calculated before use.
Many impurities are generated during forced degradation of any AIP and result in reduced purity and assay. Mass balance gives the relationship between the purity of the degraded sample and the assay.The mass balance states that the amount of impurities formed during degradation must be equal to the loss of assay value of the degraded sample.
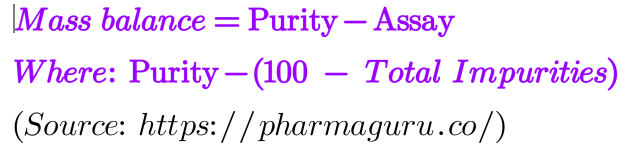
It also tells about the strength of the analytical method. The smaller the mass balance, better the analytical method. The main reason for difference in assay and purity is due to variation in the relative response factor (RRF) of different degradation products.
The following guidelines are widely used in the industries for forced degradation studies:
LCMS is required to identify and characterise the degradation impurities.
Forced degradation Studies play a critical role in pharmaceutical development by providing valuable insights into potential degradation pathways, identifying both actual and potential degradation impurities of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This knowledge is essential for ensuring drug stability, quality, and regulatory compliance. I hope this article has deepened your understanding of pharmaceutical degradation and its significance. With this foundation, you are now better equipped to independently plan, design, and conduct forced degradation studies with confidence and scientific rigour.
Related:
References
Abbreviations
Quick Links