Chiral GC (Gas Chromatography) is a separation technique used to separate enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—based on their interaction with a chiral stationary phase. Different enantiomers of a compound can have distinct biological effects, and that is the reason separation and control of unwanted isomers is essential in Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) […]
Chiral GC (Gas Chromatography) is a separation technique used to separate enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—based on their interaction with a chiral stationary phase.
Different enantiomers of a compound can have distinct biological effects, and that is the reason separation and control of unwanted isomers is essential in Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
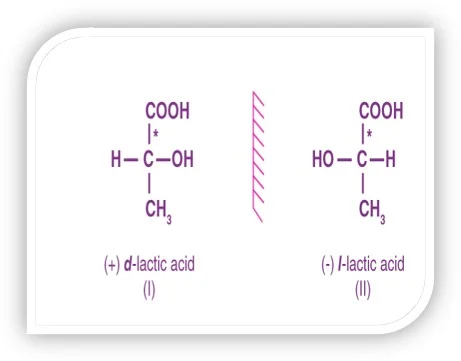
Chiral GC is a powerful technique used to separate and analyse volatile chiral pharmaceuticals.
Takeaway
Chiral GC is a separation technique used to separate enantiomers (molecules that are mirror images of each other) based on their interaction with a chiral stationary phase.
When a chiral molecule enters a GC column with a chiral stationary phase, each enantiomer interacts differently with the stationary phase. The enantiomer that interacts more strongly elutes later, while the one with weaker interaction elutes first. As they exit the column, each isomer is detected separately, producing distinct peaks on the chromatogram.
A chiral gas chromatography column contains a stationary phase and a carrier gas as a mobile phase. The enantiomer that interacts more strongly with the stationary phase elutes later, while the one with weaker interaction elutes first
Chiral GC is a type of gas chromatography specifically designed to separate chiral compounds—molecules that have non-superimposable mirror images, known as enantiomers. These enantiomers have identical physical properties but can have vastly different biological effects. This difference is especially important in the pharmaceutical industry, where one enantiomer may have therapeutic effects, and the other could be inactive or even harmful.
In standard GC, separation is based on differences in the boiling points, polarity, and volatility of the compounds being analysed. However, for chiral molecules, standard GC is not enough because enantiomers often behave the same in terms of their physical properties. Chiral GC tackles this problem by using a chiral stationary phase (CSP), which interacts differently with each enantiomer, allowing them to be separated.
You May Like
Chirality is at the heart of many chemical and biological processes. The concept of chirality has broad implications, especially in areas such as:
Many drugs, such as thalidomide, ibuprofen, and L-DOPA, are chiral compounds. Often, one enantiomer is effective, while the other can cause adverse side effects. For example, the (S)-enantiomer of ibuprofen is responsible for its anti-inflammatory effects, while the (R)-enantiomer is relatively inactive. Chiral GC is essential in the synthesis, analysis, and quality control of such drugs, ensuring that the correct enantiomer is used in the final formulation.
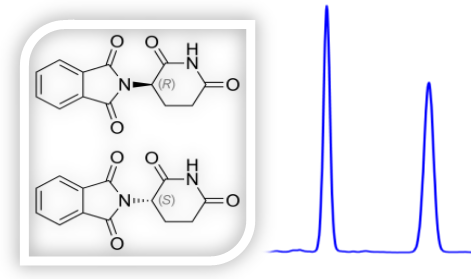
It is also used in other industries like: Food and Flavour Industry, Environmental Monitoring and Forensic Science:
The perception of taste and smell often relies on the presence of specific chiral compounds. For instance, the flavour of citrus fruits is affected by chiral molecules like limonene. Chiral GC can be used to separate and quantify these compounds to better understand their role in flavor profiles and ensure consistency in food products.
Chiral GC works on the same basic principles as conventional GC, but with a twist—literally. Here’s a breakdown of how it functions:
A small amount of the chiral compound is vaporised and injected into the chromatograph.
The vaporised sample passes through a chiral stationary phase (CSP) in the GC column. The CSP is typically made from a chiral compound that creates a chiral environment inside the column. This environment will interact differently with each enantiomer of the compound.
Enantiomers interact with the chiral stationary phase in different ways, leading to different retention times. One enantiomer may be retained longer, while the other passes through the column faster.
After separation, the compound exits the column and is detected by a detector, usually a flame ionisation detector (FID) or mass spectrometer (MS). The detector records the time it takes for each enantiomer to elute from the column, creating a chromatogram that can be analysed.
The performance of Chiral GC largely depends on the choice of chiral stationary phase. Some commonly used CSPs include:
The choice of CSP depends on the type of compounds being analyzed, as different CSPs interact differently with specific classes of chiral molecules.
While Chiral GC is a highly effective technique, it does come with some challenges:
Chiral Gas Chromatography is an indispensable tool for researchers and industries dealing with chiral compounds. Its ability to separate and analyse enantiomers with high precision has made it a cornerstone in areas such as pharmaceuticals, environmental science, food quality control, and forensic investigations. With advancements in stationary phases and detector technologies, Chiral GC continues to evolve, opening up new possibilities for understanding the molecular world around us.
Whether you’re in the lab synthesising the next breakthrough drug or monitoring environmental pollutants, Chiral GC offers a precise and reliable method to tackle the complexities of molecular chirality.
Related:
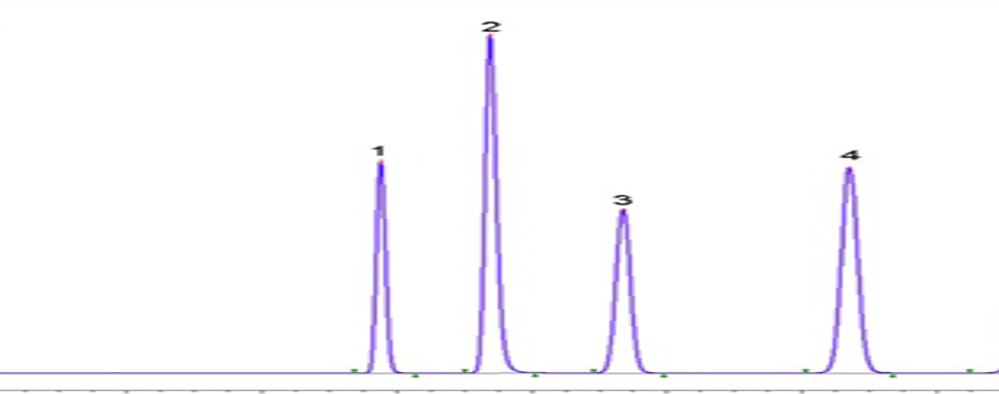
Chiral GC (Gas Chromatography) is a separation technique used to separate enantiomers—molecules that are mirror images of each other—based on their interaction with a chiral stationary phase. This method is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, where different enantiomers of a compound can have distinct biological effects, ensuring precise analysis and quality control. The figure shows the separation of a chiral molecule containing two chiral centres:
Further Reading
Quick Links