Common HPLC interview questions typically focus on fundamental concepts such as the principle of HPLC, its instrumentation, column chemistry, and mobile-phase selection. Candidates are often tested on method development, system suitability parameters, and troubleshooting skills. You should be familiar with topics like retention time, normal-phase vs. reverse-phase chromatography, isocratic vs. gradient elution, and common issues […]
Common HPLC interview questions typically focus on fundamental concepts such as the principle of HPLC, its instrumentation, column chemistry, and mobile-phase selection. Candidates are often tested on method development, system suitability parameters, and troubleshooting skills. You should be familiar with topics like retention time, normal-phase vs. reverse-phase chromatography, isocratic vs. gradient elution, and common issues such as high back pressure, baseline noise, or poor peak shape. Interviewers may also ask about the roles of the column, mobile phase, pumps, and detectors, along with the importance of calibration, system maintenance, and method validation.
In this post, I will cover all these questions with clear, concise answers to help you confidently crack your HPLC interview.
The following are the top HPLC Interview Questions with Answers:
The full form of HPLC is high-performance liquid chromatography or high-pressure liquid chromatography
HPLC (high-pressure/high-performance liquid chromatography) is a separation technique based on solid stationary and liquid mobile phases. Separations depend upon the polarity of the stationary phase, mobile phase and molecules. Separation may be achieved by either the Partition mechanism or the Adsorption mechanism
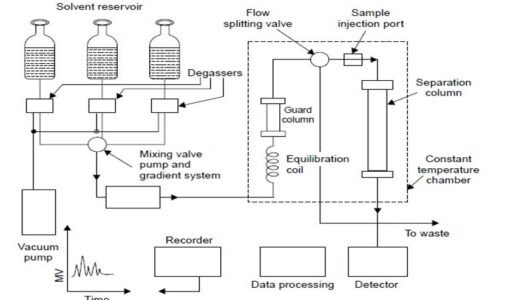
The following are the different components of HPLC:
The guard column is a short column that contains the same stationary phase as the analytical column. But in the guard is filled with bigger particle sizes to avoid any unnecessary pressure. It removes the impurities present in the buffer and solvents of the mobile phase.
The HPLC column is the heart of the HPLC, and it is responsible for the separation of different components. It is packed with the stationary phase, like C18, C8 phases.
The cyano column is a universal column in HPLC
Mobile phase in HPLC is a solvent or a mixture of solvents or a mixture of solvents containing solid buffers.
In the isocratic mode of elution composition of solvent in the mobile phase does not change or remain constant. For example, if the mobile phase is a mixture of water and acetonitrile in a composition of 60:40, it means this composition will remain the same throughout the analysis.
In the gradient mode of composition, of solvent changes with time. It is used to elute non-polar compounds. For example:
| Time (t) | A (0.1% HCOOH in water) | B (Acetonitrile) |
| 0 | 80 | 80 |
| 15 | 20 | 80 |
| 20 | 20 | 80 |
| 20.1 | 80 | 20 |
| 27 | 80 | 20 |
In RPC, the mobile phase is polar, e.g., a mixture of Water/Buffer and organic solvents like acetonitrile, methanol, ethanol, IPA, THF etc and the stationary phase is non-polar or less polar, e.g., C18 (ODS), C8, Cyno etc. The sample should be soluble in water or in a mixture of water and organic solvents.
First Benzoic acid will elute and then after Toluene will elute.
The HPLC is used in both qualitative (identification test) and quantitative analysis in the following industries:
The following detectors are used in HPLC analysis:
The selection of a Detector is based on:
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of reverse-phase chromatography:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
The following are the main reasons for filtering the mobile phase:
The general chapter of chromatography in <USP is 621>
Caffeine or Uracil can be used for calibration of HPLC
Caffeine is a stable molecule and readily available in pure form and that is why caffeine is used for the calibration of HPLC
Retention time may shift due to change due to the following reasons:
Yes. On increasing temperature retention time is decreased, and on decreasing temperature retention time is increased
Due to pressure fluctuation or improper column equilibration retention time may change in each run
The pump delivers the mobile phase at a constant, precise flow rate and generates the high pressure needed for chromatographic separation.
The detector measures the amount of analyte eluting from the column and converts it into a signal (peak) on the chromatogram.
Retention time (Rt) is the time taken by an analyte to travel from injection to detection.
RRT is the ratio of the retention time of an analyte to the retention time of a reference standard.
High back pressure is excessive system pressure caused by blockages or column issues. Troubleshooting includes: filtering the mobile phase, replacing the guard column, reversing or replacing the column, and checking for leaks or clogged frits.
Baseline drift is a gradual change in the detector baseline. Causes include temperature changes, mobile-phase composition shifts, detector lamp aging, or gradient elution.
Poor peak shape (tailing, fronting, broadening) can result from column overloading, dead volume, wrong pH, contaminated column, or incompatible mobile phase.
Use proper needle wash solvents, increase wash cycles, use strong wash solutions, maintain injector cleanliness, and avoid sticky sample matrices.
Degassing removes dissolved gases that can form bubbles, cause noise, baseline drift, or pump cavitation.
Earlier, HPLC used very high pressures, so it was called high-pressure LC. Modern systems operate under both high pressure and controlled liquid flow, so the term evolved to high-performance or simply liquid chromatography.
It includes column type, mobile phase composition, flow rate, temperature, injection volume, detection wavelength, and run time.
A chromatogram is a plot of detector response versus time showing peaks corresponding to different analytes.
A peak represents the detector response when an analyte elutes from the column.
Peak integration calculates the area under the peak, which is proportional to the analyte concentration.
Separation occurs based on differential interactions of analytes with the stationary phase and the mobile phase.
A frit is a porous metal disk that prevents packing material from leaving the column and traps particulates.
Includes verifying pump flow, leak check, mobile-phase preparation, system equilibration, wavelength accuracy, and baseline stability.
PDA (photodiode array) detectors record full UV spectra, allowing peak purity analysis, wavelength scanning, and identification confirmation.
Causes: air bubbles, pump pulsation, dirty detector cell, or loose fittings.
Solutions: degas mobile phase, purge pump, tighten fittings, clean detector cell.
RSD (%) = (Standard deviation / Mean) × 100; measures method precision.
Empower 3 has improved compliance tools, enhanced processing speed, better reporting, updated UI, and expanded data security compared to Empower 2.
Flow rate accuracy, wavelength accuracy, injector precision, detector linearity, pressure test, and gradient accuracy.
Caffeine is commonly used as a system suitability standard for wavelength accuracy and detector linearity due to its sharp UV absorbance.
System Suitability Test ensures the system performs correctly before sample analysis by checking parameters like theoretical plates, tailing factor, and resolution.
Relative Response Factor indicates the detector response of an analyte relative to an internal or reference standard.
Adjusted retention time = Retention time – Column dead time (t0); shows actual interaction time with the stationary phase.
Ghost peaks are unexpected peaks caused by contamination, previous injections, degraded solvents, or system memory effects.
Carryover is residual analyte detected in subsequent injections, usually from autosampler surfaces, injector needle, or tubing.
Boost your pharma career with PharmaGuru’s expert-led online courses.: Online Pharma Course (Training)
As a mirror tells about the beauty of the human face in the same way HPLC result tells about the quality of the pharmaceuticals. I hope this post has increased your knowledge to the next level and now you can use it more effectively in pharmaceutical development. For any query or suggestion related to this article, write in the comment section or contact me using the contact form.
You May Like
Quick Links