
The Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) concept and in silico assessment systems are powerful tools that help reduce the need for extensive toxicity testing of potential genotoxic impurities during pharmaceutical development. Managing genotoxic impurities is one of the most challenging responsibilities for pharmaceutical scientists, requiring a solid understanding of chemistry, toxicology, and regulatory expectations. In […]
The Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) concept and in silico assessment systems are powerful tools that help reduce the need for extensive toxicity testing of potential genotoxic impurities during pharmaceutical development. Managing genotoxic impurities is one of the most challenging responsibilities for pharmaceutical scientists, requiring a solid understanding of chemistry, toxicology, and regulatory expectations.
In this post, you will learn about the sources of genotoxic chemicals, the classification of genotoxic impurities, the TTC concept, and the different types, such as standard TTC and staged TTC. We will also discuss the advantages of using TTC, situations where TTC may not apply, and the role of in silico prediction tools in risk assessment.

Sources of Genotoxic Impurities
The following are the major sources of Genotoxic impurities in APIs (Active pharmaceutical ingredients):
Impurities have been classified in the following five classes:
This group includes known animal carcinogens with reliable data for a genotoxic mechanism, and human carcinogens. The genotoxic nature of the impurity is demonstrated using published data on the chemical structure. Impurities of this class having compound specific limit.
This group includes impurities with demonstrated mutagenicity based on testing of the impurity in conventional genotoxicity tests. Impurities of this class is controlled at threshold limit called TTC (Threshold of toxicological concern)
This group includes impurities with functional moieties that can be linked to genotoxicity based on structure. However, these moieties have not been tested as isolated compounds and are identified based on chemistry and using knowledge-based expert systems for structure activity relationships (SAR). Impurities of this class is controlled at threshold limit called TTC.
Impurities of this class are treated similar as API.
Although genotoxic impurities are classified, the major challenge is to design strategies to control these genotoxins. The major challenges were regarding Class 2 and Class 3 inaccuracies. Now the question is: Can these genotoxins show genotoxicity at all levels? If yes then what is the solution and if not, at what levels will these Genotoxins be controlled? We are going to discuss the same in the TTC concept section.
In 1958, the Delaney Rule stated that “No food or colour additive shall be deemed safe if it is found to induce cancer in humans or animals.” This clause, introduced by Congressman James Delaney, was part of the 1958 Food Additives Amendment to the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938.
However, as analytical technologies advanced and became far more sensitive, it became possible to detect extremely low levels of chemicals—sometimes in the parts-per-billion or parts-per-trillion range. This created a challenge:
even substances that could potentially cause cancer at high doses were being detected at very low concentrations used, for example, as preservatives—levels far below any realistic risk.
The U.S. FDA was the first regulatory agency to encounter this dilemma, particularly in relation to diethylstilbestrol (DES). The situation highlighted the need for a more practical, science-based approach to evaluating risk from trace-level exposures.
This ultimately contributed to the development of the Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) concept, which provides a rational framework for determining when low-level exposures to potentially harmful chemicals are unlikely to pose a significant risk.
Diethylstilbestrol was being used to increase the shelf life of meat in the meat industry. It addressed the issue by using quantitative risk assessment, declaring that if a carcinogenic food additive was present at a concentration of less than 1 part in 1,000,000, the risk was negligible.
This standard became known as the “exceedingly low /de minimis” exception to the Delaney Rule and was used throughout the FDA and other agencies. Using this concept threshold of Genotoxins was proposed.
A TTC-based acceptable intake of a mutagenic impurity of 1.5 µg per person per day is considered to be associated with a negligible risk (theoretical excess cancer risk of <1 in 100000 over a lifetime of exposure) and can in general, be used for most pharmaceuticals as a default to derive an acceptable limit for control. This approach would usually be used for mutagenic impurities present in pharmaceuticals for long-term treatment (> 10 years) and where no carcinogenicity data are available (Classes 2 and 3).
This concept is called the TTC (threshold of toxicological concern) concept.
1.5 μg/day is being considered acceptable where compound specific tox data are not available. This is also called the registration limit.
Boost your pharma career with PharmaGuru’s expert-led online courses.: Online Pharma Course (Training)
In standard TTC, the permitted level in the Active substance is calculated by the following formula:
Permitted level in active substance (in ppm) = TTC/ Maximum daily Dose (in grams)
Rilpivirine, Max dose = 25mg
Permitted GI in Rilpivirine(in ppm) = 1.5/ 0.025 (in gram) = 60 ppm
Since the TTC value is calculated for lifetime exposure and consequently, it was decided to allow higher levels for treatments of shorter duration. This concept is called Staged TTC. It is accepted into the clinical development phase.
EMEA limits based on 70-year exposure assumptions:
Lifetime exposure allowed will be 38.33 mg by the following is the calculation:
1.5x (70 years x 365 days) = 38.33mg
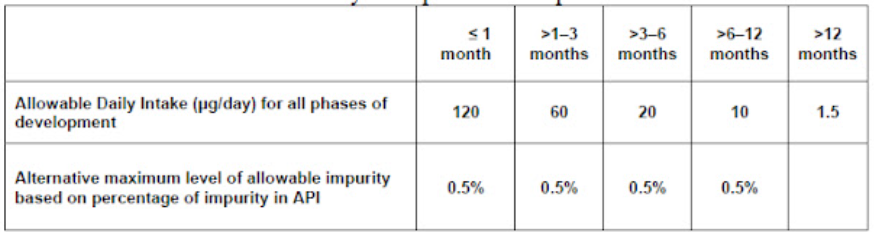
The above allowable daily intake for Staged TTC may be calculated by following formulae:
The following are the advantages of the TTC:
The following high-potency Carcinogens are excluded from the TTC approach:
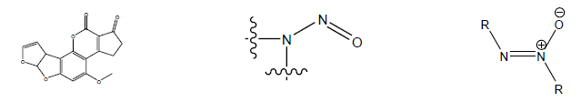
The above structural groups were identified to be of such high potency that intakes even below the TTC would theoretically be associated with a potential for a significant carcinogenic risk. This group of high-potency mutagenic carcinogens is referred to as the cohort of concern.
A TTC value higher than 1.5 μg/day may be acceptable under the following conditions:
Several systems are available for Genotoxic evaluation and out of them the following systems are widely used in the Pharmaceutical industries:
The following are the advantages of the in silico predictions:
The following information is required for Insilco predictions:
I spite of various challenges, the TTC concept and In-silico approach are very helpful during drug development. Hope this post has cleared all your doubts related to the TTC concept and the In-silico system. Write your learning and questions related to this post in the comment section.
Together, these approaches form a modern, efficient framework for managing genotoxic impurities during drug development.
You May Like
The different sources of Genotoxic impurities are raw materials like SM. KSM, chemicals,, solvent and reagents used in the process. Genotoxic impurities may form in the process also
A TTC-based acceptable intake of a mutagenic impurity of 1.5 µg per person per day is considered to be associated with a negligible risk (theoretical excess cancer risk of <1 in 100000 over a lifetime of exposure) and can in general be used for most pharmaceuticals as a default to derive an acceptable limit for control
1.5 µg per person per day
The following are the TTC values for Cramer classes I, II and III
| Creamer class | TTC value |
| Cramer class-I | 30μg/kg bw per day |
| Cramer class-II | 9μg/kg bw per day |
| Cramer class-III | 1.5μg/kg bw per day |
TTC is an approach aimed at reducing extensive toxicity evaluations
A TTC value higher than 1.5 μg/day may be acceptable in conditions like When life expectancy is less than 5 years, short-term exposure etc.
Insilco system is used to evaluate the genotoxic nature of a molecule based on its structure. It reduces the drug development cost.
There are several systems available to predict the genotoxic nature of a chemical, and for some molecules, they don’t provide uniform results. It has also been observed many times that different versions of the same system predict unimaginable results. This put scientists in a difficult situation
The structural groups Aflatoxin-like, Nitroso amines and Azoxy-compounds shows carcinogenic nature even below the TTC level. This group of high-potency mutagenic carcinogens is referred to as the cohort of concern.
Not all chemicals qualify for the standard TTC value of 1.5 μg/day (for DNA-reactive genotoxic impurities).
Some structural classes are considered high-risk and require case-specific evaluation. These are known as the Cohort of Concern (CoC).
The Cohort of Concern includes:
For chemicals in the Cohort of Concern, the TTC approach cannot be applied because even ultra-low exposures may pose risk. Instead, stricter limits or compound-specific toxicological assessments are required.
In silico prediction tools (such as QSAR models) are essential in modern TTC-based risk assessment. They help classify genotoxic impurities quickly, without requiring long-term animal studies.
In silico systems assist with:
By combining TTC limits with in silico predictions, pharmaceutical scientists can make faster, more reliable, and more ethical decisions about impurity control
Quick Links