Both Impurities And Related Substances degrade the quality of a pharmaceutical. Pharmaceutical impurities are unwanted substances found in a drug product, including residual starting materials, by-products, reagents, and degradation products. Related substances are a specific category of impurities that are structurally similar to the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), typically arising from the manufacturing process or […]
Both Impurities And Related Substances degrade the quality of a pharmaceutical.
Pharmaceutical impurities are unwanted substances found in a drug product, including residual starting materials, by-products, reagents, and degradation products. Related substances are a specific category of impurities that are structurally similar to the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), typically arising from the manufacturing process or during drug degradation.
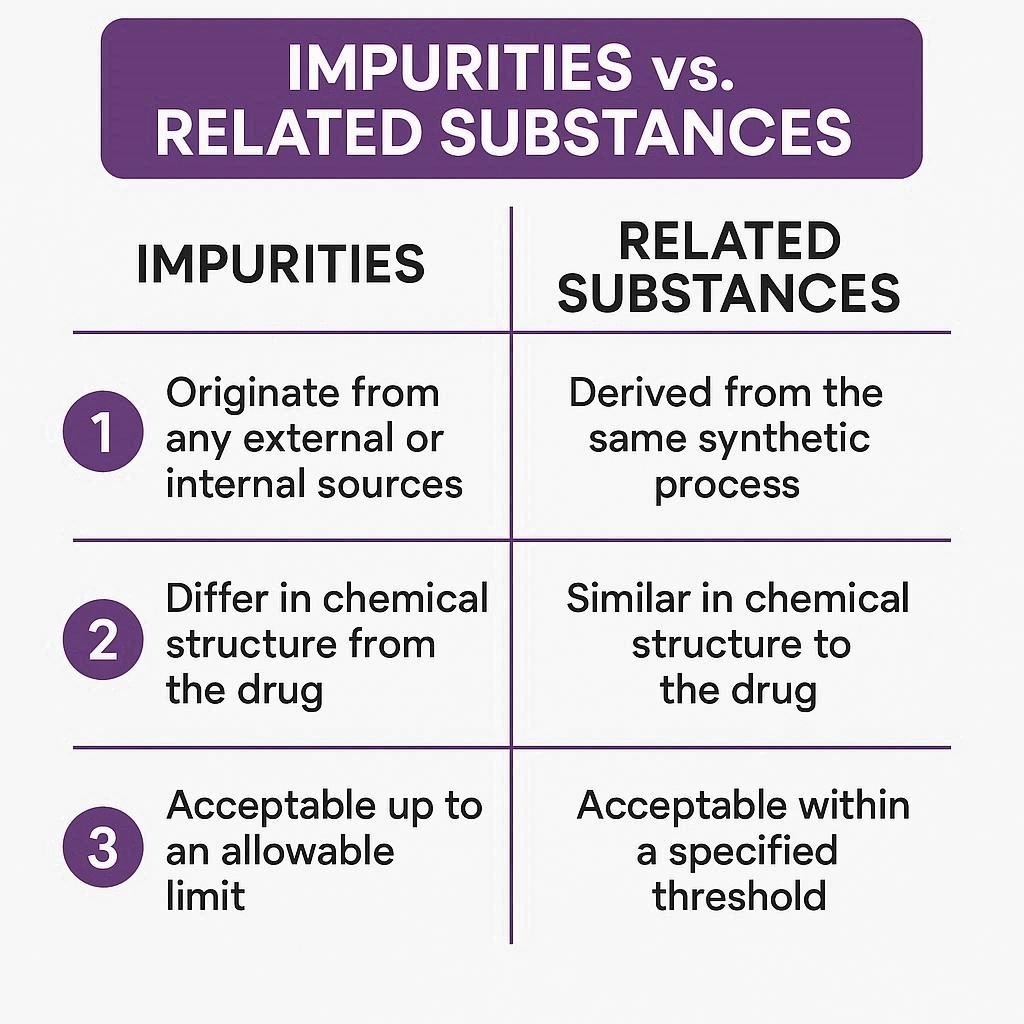
Impurities refer to any unwanted chemicals present in a drug product, whether or not they are related to the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
Related substances are a subset of impurities that are structurally similar to the API, such as isomers, degradation products, or synthetic intermediates.
Impurities and related substances can impact drug safety, efficacy, and shelf life. Some may be toxic, reduce potency, or cause unexpected side effects. Regulatory agencies require strict control of these substances to protect patient health.
Common sources include:
1. Residual solvents from synthesis
2. Reagents and catalysts
3. Degradation due to light, heat, or moisture
4. Leachables from packaging
5. Contaminants from raw materials
Related substances are typically identified using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), or NMR. They are quantified against known standards and compared to pharmacopeial limits.
The primary guidelines include:
1. ICH Q3A: For impurities in drug substances
2. ICH Q3B: For impurities in drug products
3. Limits are based on daily dosage, toxicity data, and qualification thresholds.
Unspecified impurities are those not individually listed in the specification but still detected during testing. If present above threshold levels (typically 0.1%), they must be identified, characterised, and qualified as per regulatory guidelines.
Pharmaceutical impurities are unwanted chemicals that remain in a drug substance or product, arising from manufacturing, storage, or degradation processes.
You May Like
| Aspect | Impurities | Related Substances |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Any component in the drug substance or product that is not the desired active ingredient or excipient. | Chemically related compounds that are structurally similar to the drug substance, including impurities, degradation products, and process-related materials. |
| Scope | It can affect drug potency, stability, and cause toxicity or adverse reactions. | Narrower – focuses on compounds structurally related to the API (active pharmaceutical ingredient). |
| Sources | – Synthesis by-products – Degradation – Raw materials – Residual solvents – Packaging interactions | – Process-related substances – Degradation products – Isomers or analogs of the API |
| Classification | – Organic impurities – Inorganic impurities – Residual solvents – Degradation products | – Specified related substances – Unspecified related substances – Total related substances |
| Detection Methods | – HPLC – GC – LC-MS/MS – UV-Vis Spectroscopy – NMR – Titration for inorganic | – Primarily HPLC and LC-MS, focusing on structurally similar compounds |
| Regulatory Guidelines | ICH Q3A (Impurities in new drug substances) ICH Q3B (Impurities in new drug products) | ICH Q3A/Q3B includes related substances under the umbrella of impurities; also specified in pharmacopeial monographs |
| Examples | – Benzene (residual solvent) – Heavy metals – Acetic acid from synthesis – Hydrolytic degradation products | – EP Impurity A/B/C for Paracetamol – Isomers of drug – Dimeric forms of the API |
| Impact on Drug Safety | Limits are usually specified for each related compound in pharmacopeias and based on structure-activity relationships | May retain partial activity or introduce unexpected effects, compromising safety or efficacy. |
| Limit Criteria | Set based on ICH thresholds (e.g., 0.1% for individual impurities) and toxicity data | Limits are usually specified for each related compound in pharmacopoeias and based on structure-activity relationships |
Further reading:
Quick Links