
A Pharmaceutical Technical File is a detailed compilation of documents that prove a product’s compliance with applicable regulations and standards. It is a mandatory requirement for many products, especially those requiring CE marking within the European Union. The file serves as crucial evidence of the product’s safety, efficacy, and overall performance. The Technical File document […]
A Pharmaceutical Technical File is a detailed compilation of documents that prove a product’s compliance with applicable regulations and standards. It is a mandatory requirement for many products, especially those requiring CE marking within the European Union. The file serves as crucial evidence of the product’s safety, efficacy, and overall performance.
The Technical File document acts as a central point of reference and holds detailed information regarding the pharmaceutical, its production, quality control, and much more.
In this blog post, I will discuss the definition, purpose, types, content, examples, and the advantages of the Technical File in the pharmaceutical industry. We’ll also provide guidance on how to prepare and maintain it.
Major Takeaway
A Technical File is a comprehensive compilation of all technical documentation required by regulatory authorities to demonstrate that a pharmaceutical product meets the required standards for safety, efficacy, and quality. This file is crucial during the product registration process and may be requested during inspections, audits, or product reviews.
To write a technical file for an API, include:
1. General info (name, structure)
2. Manufacturing process & controls
3. Impurity profile & characterisation
4. Specifications & test methods
5. Stability data
Follow ICH CTD format and ensure regulatory compliance.
A Technical File is a comprehensive compilation of all technical documentation required by regulatory authorities to demonstrate that a pharmaceutical product meets the required standards for safety, efficacy, and quality. This file is crucial during the product registration process and may be requested during inspections, audits, or product reviews.
The technical file serves as evidence that the product complies with regulatory requirements, including manufacturing processes, safety evaluations, and labelling specifications. For instance, a Technical File is often required when a pharmaceutical company seeks approval from regulatory bodies such as the FDA (U.S.), EMA (European Medicines Agency), or TGA (Australia).
You May Like
The primary purposes of the Technical File are:
The following are the different types of Technical Files in the Pharmaceutical Industry:
An Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Technical File should comprehensively document the identity, quality, safety, and manufacturing of the drug substance. It typically includes the following sections:
1. General Information
3. Scientific and Development Data
4. Chemical Structure and Characterisation
5. Physical and Chemical Properties
6. Manufacturing Information
7. Impurities
8. Stability
9. Storage and Handling
10. Safety Information
11. Patent and Regulatory Status
12. Bibliography and References
The technical file is an important document that includes all necessary information related to API development and analysis. It is shared with the customer by the regulatory department to review whether the API meets their requirements.
1. Introduction
This case study describes the compilation of an API Technical File for Paracetamol, a widely used analgesic and antipyretic drug substance. The objective of the technical file is to demonstrate that the API is consistently manufactured, well-characterised, stable, and safe for use in pharmaceutical formulations, in compliance with international regulatory requirements such as ICH Q7 and CTD Module 3.2.S.
2. General Description of the API
3. Specifications and Routine Tests
The API specifications were established based on pharmacopoeial requirements (USP, BP, Ph. Eur.).
Routine quality control tests include:
Acceptance criteria comply with pharmacopoeial limits, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency.
4. Scientific and Development Data
Development chemistry studies focused on optimising yield, purity, and environmental safety. Process parameters such as reaction temperature, solvent selection, and purification steps were refined to minimise impurities and ensure reproducibility.
Scientific justification was provided for:
5. Evidence of Chemical Structure
The chemical structure and identity of Paracetamol were confirmed using:
These data collectively confirmed the molecular structure, functional groups, and molecular weight of the API.
6. Physical and Chemical Properties
These properties were documented to support formulation development and stability evaluation.
7. Manufacture
Paracetamol is manufactured at a GMP-compliant facility approved by regulatory authorities.
7.2 Synthetic Route
The API is synthesised via acetylation of p-aminophenol using acetic anhydride, followed by crystallisation and purification. A detailed flow diagram and narrative description of each step are included in the technical file.
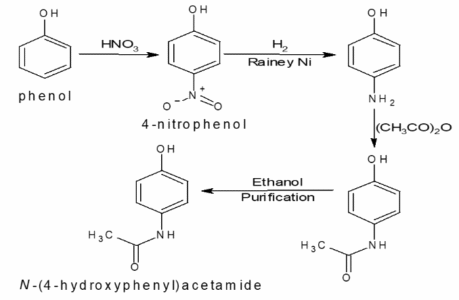
7.3 Development Chemistry
Process development focused on controlling reaction completeness and reducing by-product formation. Critical steps were identified and monitored to ensure consistent quality.
8. Impurities
The impurity profile includes:
Impurity limits were established based on toxicological evaluation and ICH Q3A/Q3C guidelines.
9. Stability
Stability studies were conducted under long-term and accelerated conditions according to ICH Q1A guidelines.
Results demonstrated that the API remains within specification throughout the proposed retest period.
10. Storage and Handling
11. Safety Information
A Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS / SDS) is included, detailing:
Paracetamol is classified as low hazard under normal handling conditions.
12. Patent Status
Paracetamol is off-patent. A freedom-to-operate assessment confirmed no active patent restrictions affecting manufacture or sale.
13. Bibliography
The technical file references:
14. Summary
The API Technical File for Paracetamol provides comprehensive documentation of the drug substance’s identity, manufacturing process, quality controls, stability, and safety. The compiled data demonstrate compliance with international regulatory standards and support the use of Paracetamol as a high-quality API for pharmaceutical products.
The Technical File is an essential part of the pharmaceutical product lifecycle, from development through to market entry and beyond. It serves as a vital tool for ensuring regulatory compliance, safeguarding product quality, and facilitating smooth communication with regulatory bodies. Companies must take great care in assembling, updating, and maintaining their Technical Files to ensure a successful product launch and long-term success in the market.
Further Reading
Quick Links