Learn the importance of System Suitability Testing (SST) in chromatography for HPLC, GC, LCMS, and more. Discover how to establish SST criteria, evaluate system performance, and avoid common pitfalls during method development.
System suitability test (SST) is an important procedure that evaluates whether a chromatographic system ( such as HPLC, GC, LC-MS, GC-MS, or TOC) is capable of producing accurate and reliable results.
Before performing routine samples or standard injections, a system suitability test solution is first injected into the system, and the results are evaluated against pre-defined criteria. Only if these criteria are met can further analysis proceed.
In chromatographic techniques like HPLC and GC, SST is more than just a regulatory requirement; it’s a safeguard for data accuracy and system performance. During method development, deciding on appropriate SST criteria can be a challenging task for chromatographers. A small error in this process can result in major failures.
In this article, I aim to explain the complexities of SST, and use my experience to guide you through the process. I’ll walk you through key concepts such as how to establish SST criteria, the role of system suitability solutions and SST markers, the acceptance criteria for SST, and common pitfalls to avoid. I’ll also provide real-world case studies and answer some frequently asked questions, giving you the tools you need to confidently determine SST during method development and make your chromatography analysis more reliable.
By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to not only meet industry standards but also to improve your method development process, ensuring your analyses are accurate, reliable, and regulatory-compliant.
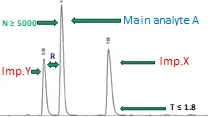
The System Suitability Test (SST) is a key procedure that evaluates whether a chromatographic system is capable of producing accurate and reliable results. During method development, several critical parameters are assessed, including the elution order of components, peak shape, resolution, and reproducibility. The SST ensures that the system, comprising the column, detector, and other components, meets predefined criteria to deliver consistent and precise measurements. Key chromatographic parameters that influence system performance, such as retention time, peak symmetry, and signal sensitivity, are carefully considered when establishing the SST acceptance criteria.
Related:
Relative Response Factor (RRF) in Pharmaceutical Analysis: Learn In 5 Steps
The following chromatographic parameters are used to define the system suitability test:
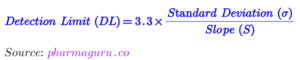
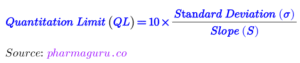
The analyte used for the system suitability test must have the following characteristics:
The system suitability test must contain at least two chromatographic parameters. Generally, 2 to 5 chromatographic parameters are kept in the system suitability test. The system suitability test solution is prepared by using an individual analyte standard. The SST marker standard is also used to prepare the system suitability solution.
The SST solution is prepared as a method and is injected into the chromatographic system to assess its performance. For instance, in pharmaceutical analysis, the SST solution might contain known amounts of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and related impurities.
System suitability marker contains all the components on which SST is decided.
If the process contains impurities of different polarities (polar, intermediate polar and nonpolar ) in that case retention time (RT) marker is used as a system suitability test standard.
I recommend using RT marker as an SST standard since this approach is cost effective and it avoids all confusion related to variation in the retention time.
Other chromatographic parameters, like precision and signal-to-noise ratio, can be included in the system suitability test.
| System suitability test parameter | The obtained value | Acceptance criteria | Remarks |
| Resolution (R) | 3 (≥1.5) | The Column efficiency for the main analyte (A) should be more than or equal to 4000 | Complies |
| Column efficiency (N) | 5000 (≥4000) | The Tailing factor for the main analyte (A) should be less than or equal to 1.8 | Complies |
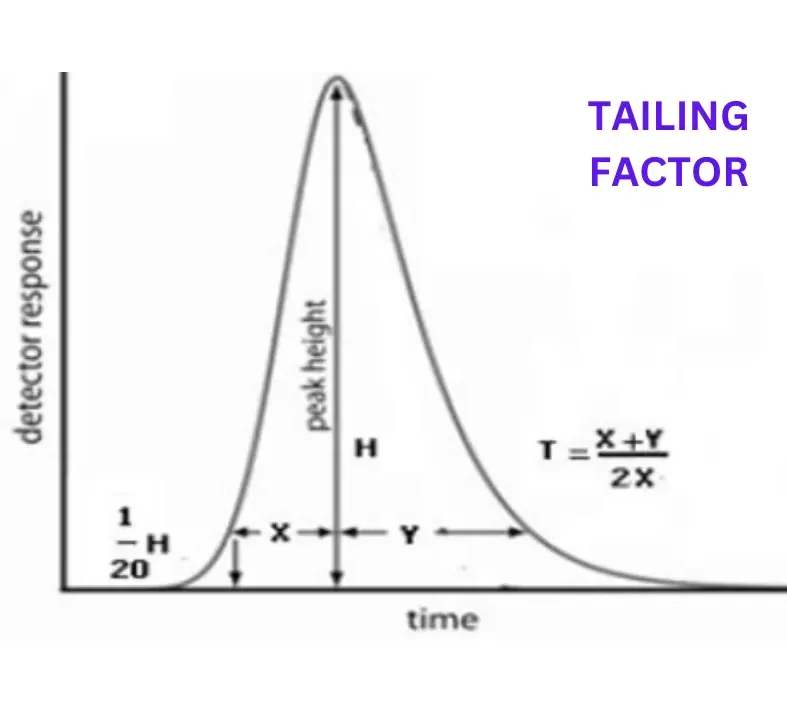
| Tailing factor (T) or symmetric factor | 1.3 (≤1.8) | The S/N for the sensitivity solution should be more than or equal to 10 | Complies |
| S/N or signal to noise ratio | 21 (≥10) | S/N or signal-to-noise ratio | Complies |
| RSD | 0.7 %(≤2.0%) | The RSD of the area response of main analyte (A) of six replicates should be less than or equal to 2.0 | Complies |
| Component name | RTs (minutes) | RRTs | Remarks* |
| Main analyte A | 5.4 (limit: about 5) | 1 | Complies |
| Imp. X | 7.7 (limit: about 8) | 1.54 (limit: about 1.5) | Complies |
| Imp.Y | 10.4 (limit: about 10) | 2.08 (limit: about 2) | Complies |
*Note: Refer to this post to handle variation in RTs and RRTs
Use the following best practices for the system suitability test :
Regulatory agencies like the FDA, KFDA, and TGA are more cautious about the system suitability testing. System suitability test must be decided scientifically and based on the trend data from multiple lots. The method must contain at least two system suitability parameters
A drug substance A contains 3 impurities. Main impurity elutes at 5 minutes, impurity B elutes at 6.5 minutes, impurity C elutes at 10 minutes, and impurity D elutes at 25 minutes. What should be the system suitability criteria?
Since the main analyte A and impurity B elute adjacent to each other. Hence, one of the system suitability parameters will be resolution (R). Column efficiency or tailing factor may be kept second system suitability test parameter. Since this is the impurity profile method and hence Quantitation limit will also be part of the system suitability test, and acceptance criteria will be decided based on the S/N ratio. The acceptance criteria of the system suitability will be decided based on the trend data of several lots.
In a drug substance X, having assay limit 98 to 100%w/w. Drug substance X elutes at 6 minutes, and its impurity A elutes at 30 minutes. What should be system suitability criteria?
Since impurity A peak elutes far away from the drug substance peak X and therefore Resolution can not be kept in the system suitability test. The system suitability can be decided using column efficiency and tailing factor. Precision will also be part of the system suitability
If the system suitability test is inadequate, it may
System Suitability Testing (SST) is crucial for assessing the performance and reliability of chromatographic systems, ensuring that your method delivers accurate and consistent results. Deciding on the appropriate SST criteria requires both a strong foundation of knowledge and practical experience. I hope this article has clarified any uncertainties and empowered you to confidently define SST acceptance criteria for any chromatographic method.
If you have any feedback, questions, or suggestions related to this article, feel free to share them in the comments section below. For further assistance or personalised guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out via the contact form.
You may also want to check out other articles on my blog, such as:
SST or system suitability test decides whether the HPLC system is suitable or not to give the correct result. SST contains two or more than two analytes. SST acceptance criteria should be decided using at least two chromatographic parameters.
SST check decides whether the chromatographic system is suitable or not to give the correct result. SST contains two or more than two analytes.
The chromatographic parameters like resolution, column efficiency and tiling factor are used in SST in GC b
The system suitability test tells whether the chromatographic system is suitable or not to give the correct result. SST contains two or more than two analytes. SST acceptance criteria.should be decided using at least two chromatographic parameters
The system suitability test solution is prepared by using two or more than two analytes. In some of the method SST marker standard is used to prepare the system suitability solution.
The USP limit for the tailing factor is between 0.8 to 1.8
System suitability marker contains all the analytes which decide system suitability acceptance criteria. It may be prepared in the lab or commercial SST marker can be used (if available)
System suitability test acceptance criteria must contains at least two chromatographic parameters
You can explain the troubleshooting steps (e.g., checking the system for leaks, optimising flow rate, or column replacement) while using HPLC
Is it just during method development, or should it be checked periodically throughout routine analyses?
Many modern instruments come with built-in SST checks.
References
Abbreviations
Quick Links