Learn how to evaluate specificity during analytical method validation in pharmaceutical analysis. Includes step-by-step procedures, acceptance criteria, case study, and FAQs.
Specificity In Analytical Method Validation tells about the the efficiency of the analytical method or in other words capability of the method to separate different components like main analyte peak and impurity peaks.
Specificity is a critical parameter in the validation of analytical methods, particularly in pharmaceutical analysis. It ensures that the method can accurately measure the analyte of interest in the presence of potential interference such as impurities, degradation products, matrix components, or excitements. In this article, we will walk through the complete procedure for evaluating specificity, including sample and standard preparation, injection procedures, acceptance criteria, and a real-world case study. Additionally, we’ll cover frequently asked questions to help you address common challenges. By the end of this post, you will be equipped to confidently apply these steps during method validation or development.
Specificity tells about the the efficiency of the analytical method or in other words capability of the method to separate different components like main analyte peak and impurity peaks.
You may like: How To Control Impurities In Pharmaceuticals: Get Mastery In …
Standard and sample preparation
Injection procedure
Inject the following solutions in the HPLC system containing a PDA or DAD detector and generate the chromatogram as per chromatographic condition given in the method::
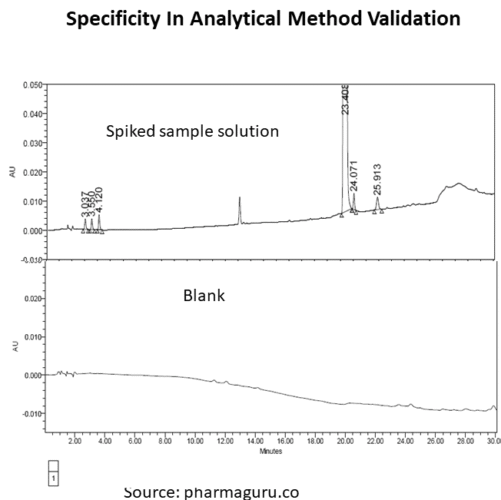
Case study
Let us consider the following are the related substances specification of an API and we have to perform specificity test:
The sample concentration in the method is 1000 mcg/ml
Standard and sample preparation
Acceptance criteria
In Stability indicating method validation sample is exposed to the following stress conditions to perform the specificity test:
| Specificity | Selectivity |
| Specificity deals with the separation of peak of interest with the adjacent component peak or impurity peak | Selectivity deals with the separation between each components in the chromatogram |
| In specificity, there should not be any interference of any peak with the peak of interest | In selectivity, there should not be any interference between each component |
| In the assay method, there should not be any interference of impurity peak with main peak. There may be interference between the impurities peaks | In the Related substances method, there should not be any interference between impurities peak and between main peak and impurity peak |
Related Topic: What Is Analytical Method Validation In Pharmaceutical Analysis: Learn In 11 Minutes
Specificity is a fundamental aspect of analytical method validation, ensuring that the method can accurately measure the target analyte without interference from other components. By following the outlined procedures for sample and standard preparation, injection, and evaluation against defined acceptance criteria, analysts can confidently establish the reliability of their methods. Incorporating specificity studies during both method development and validation not only supports regulatory compliance but also enhances the overall robustness and accuracy of pharmaceutical analysis.
You may also want to check out other articles on my blog, such as:
You may also want to explore other related articles on my blog, such as:
Specificity tells about the efficiency of the method to separate peak of interest from the adjacent component peak. Secondly, there should not be any interference of diluent peak with the peak of interest
Specificity deals with the separation of the peak of interest from the adjacent component peak or impurity peak. Selectivity deals with the separation between each component in the chromatogram.
For example assay method is specific whereas the related substance method is selective
There should not be any interference of the main peak or assay peak with any impurity peak or diluent peak.
The peak of interest must be separated from other component peaks or diluent peak
Specificity tells about the efficiency of the method to separate peak of interest from the adjacent component. There should not be any interference of diluent peak with the peak of interest. Sensitivity tells about the capacity of detector to quantify lowest amount of analytes. For sensitivity, the ratio of signal to noise (S/N) should be more than or equal to 10
No. Specificity is related to the separation of the main component from the other component peaks whereas accuracy is related exactness of the method to quantify the analyte
Quick Links