ppm, mcg and percentage are the units of measurement and play a crucial role in pharmaceutical development. In both synthetic and analytical chemistry, precise measurements are key to accurate sample preparation and analysis. Among the most frequently used units in this process are ppm, mcg/µg, and % – terms that, while common, often lead to […]
ppm, mcg and percentage are the units of measurement and play a crucial role in pharmaceutical development.
In both synthetic and analytical chemistry, precise measurements are key to accurate sample preparation and analysis. Among the most frequently used units in this process are ppm, mcg/µg, and % – terms that, while common, often lead to confusion for many chemists. Whether you’re an analytical chemist or working in quality control, a solid grasp of these units is essential for effective work.
The goal of this post is to clarify any uncertainties you may have about these terms and to provide you with the knowledge to confidently answer questions like:
By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to navigate these concepts with ease and apply them confidently in your day-to-day work.
You may like:
ppm, mcg and percentage play a crucial role in pharmaceutical development in both synthetic and analytical chemistry.
ppm stands for parts per million, or out of 1000000 or out of 10⁶. This is a mode of expressing the presence of a substance ( at a very low concentration) in the main substance, such as the presence of an impurity in a drug substance. It is a dimensionless quantity. Examples:
ppm is generally used to keep the specification of an impurity in the main Analyte or API. It is expressed in terms of weight by weight (w/w) and volume by volume (v/v).
It stands for microgram. It is the unit of weight. It is expressed as weight by volume
It stands for microgram out of 1 ml or microgram per ml. mcg/ml or µg/ml is used to specify the concentration in solution and not to specify the impurity limit.
Example:
%=(ppm/1000000)×100 or
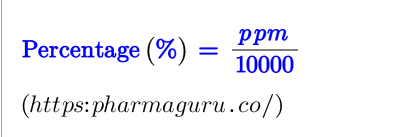
%=(5000/1000000)×100=0.5%
ppm is relative to the main compound, whereas mcg/ml is relative to the solvent used for dilution. Secondly, ppm is denoted in w/w or v/,v whereas mcg is denoted in w/volume.
mcg (microgram) and ppm (parts per million) are both units used to express concentrations, but they are used in different contexts and have different meanings.
mcg (microgram):
ppm (parts per million):
If you have 1 ppm of a substance in water, it means you have 1 mcg of that substance in 1 liter (1000 mL) of water.
To convert micrograms (mcg) to milligrams (mg), you can use the following relationship:
1 milligram (mg) = 1,000 micrograms (mcg)
So, to convert mcg to mg, divide the number of micrograms by 1,000.
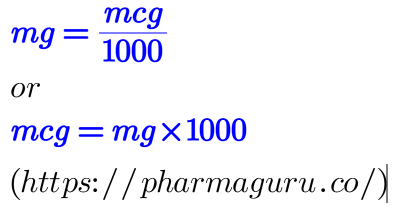
Example: If you have 500 mcg, to convert it to mg, it will be 500/1000 = 0.5mg
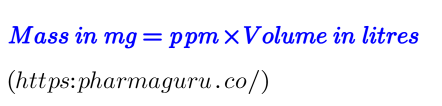
Case Study: if you have a concentration of 10 ppm in 2 litres of water:
Mass in mg = 10 ppm×2 L=20 mg
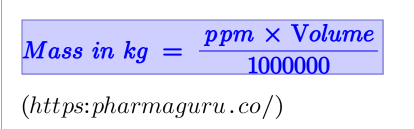
Case study: if the concentration is 10 ppm in 2 liters: (10 × 2) ÷ 1000000 = 0.00002kg
% stands for parts per 100 or out of 100 or out of 10²
This is a crucial topic, as a clear understanding of units like ppm, mcg, and % is essential across all types of analytical techniques – including chemical analysis, HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography), GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry), and more. Mastery of these units ensures precision and reliability in every step of the analysis.
I hope this post has helped clarify your doubts and deepened your understanding of This is a crucial topic, as a clear understanding of units like PPM and µg is essential across all types of analytical techniques—including chemical analysis, HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography), GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry), and more. Mastery of these units ensures precision and reliability in every step of the analysis.
I hope this post has helped clarify your doubts and deepened your understanding of PPM, µg, and related units. If you found this helpful, I encourage you to share your learnings or any remaining questions in the comments. Your feedback motivates me to continue creating more skill-focused content for the chemistry community, and related units. If you found this helpful, I encourage you to share your learnings or any remaining questions in the comments. Your feedback motivates me to continue creating more skill-focused content for the chemistry community.
Related Topics:
Parts per million
By dividing 1000000.
It means 1 ppm is equal to 1/1000000 mg or 0.000001mg
pm and mcg both are same. ppm is used to specify impurity or a substance (at low concentration) in the main substance whereas mcg/ml is used to specify the dilution
ppm and mcg both are same. ppm is used to specify impurity or a substance (at low concentration) in the main substance whereas mcg/ml is used to specify the dilution
Following is the relationship between % and ppm
%=(ppm/1000000)×100.
Therefore 1 ppm is equal to 0.0001%. It means a drug substance contains 1 ppm of Benzene (as a impurity) and a drug substance contains of Benzene (as a impurity) 0.0001% are same.
The following is the relationship between % and ppm
%=(ppm/1000000)×100. Therefore 100 ppm is equal to 0.01%.
Yes
1 mg is equal to 1000000 ppm
Yes. ppm is a relative value and it is used to specify impurity or a substance (at low concentration) in the main Drug substance/ main Analyte whereas mg and Kg are absolute terms.
1 ppm is equal to 1/1000000 mg or 10-6 mg or 10-18 Kg. For example Paracetamol drug substance having toluene as an impurity and its value is 1 ppm. We can say paracetamol have 1 ppm of toluene or 10-6 mg of toluene or 10-18 Kg of toluene.
Abbreviations:
Quick Links