Polarimeter A polarimeter is an analytical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of an optically active substance. Optically Active Substance A substance is optically active if it can rotate the plane of polarised light. It is of two types: Dextrorotatory and Levorotatory Optical Activity depends upon the Molecular structure (presence of chiral centres), Wavelength, temperature and solvent […]
A polarimeter is an analytical instrument used to measure the optical rotation of an optically active substance.
Optically Active Substance
A substance is optically active if it can rotate the plane of polarised light. It is of two types: Dextrorotatory and Levorotatory
Optical Activity depends upon the Molecular structure (presence of chiral centres), Wavelength, temperature and solvent
SOR is calculated by using the following formula-1:
Formula-1
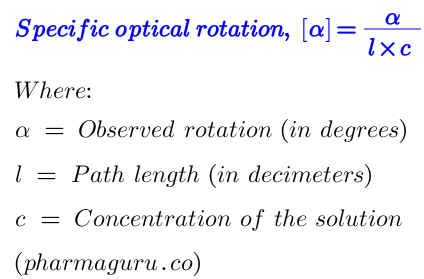
Note:
Boost your pharma career with PharmaGuru’s expert-led online courses.: Online Pharma Course (Training)
Optical purity is a measure of the amount of one enantiomer in excess over the racemic mixture. It is calculated by the following formula-2 using the polarimeter:
Formula-2:

A pharmaceutical company is developing a chiral drug where only one enantiomer is biologically active. The inactive (or harmful) enantiomer must be minimised.
Objective: Determine the optical purity of a synthesised sample using a polarimeter.
Procedure:
Calculation:
Observed rotation α = +30°
Specific rotation [α]=(30/1 x 0.6) = 50° (Using formula-1)
Enantiomer’s specific rotation is +50°
Let’s recalculate optical purity using the correct logic:
Optical purity = (30/50) x 100 = 60% (Usimg formula-2)
The enantiomeric excess is 60%, indicating that the drug contains 80% of the desired enantiomer and 20% of the undesired one.
A quality control team at a juice manufacturing company wants to verify the sugar content using polarimetry, as sugar is an optically active substance.
Objective: Determine the concentration of sucrose in a juice sample.
Procedure:
c = (α/[α] xl) = (13.2/66.5 x2) = 0.0992 g/mL
Multiply by 1000 to convert to g/L: 0.0992×1000=99.2 g/L
Note: The sugar concentration in the juice sample is approximately 99.2 g/L, matching the expected sweetness and caloric content.
In conclusion, the polarimeter is a vital tool in analysing optically active substances by measuring the angle of optical rotation. Understanding its working principle, methods for calculating specific optical rotation and optical purity, along with practical case studies, provides valuable insight into its applications in fields such as chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and food science. The FAQs further clarify common doubts, making this article a comprehensive guide to the use and significance of polarimetry.
Related
To measure the angle of rotation of polarised light caused by optically active substances, which helps identify enantiomers and assess purity
No. A racemic mixture contains equal amounts of both enantiomers and thus hano net optical activity.
Traditional polarimeters use sodium D line emission at 590 nm, and modern laser polarimeters use laser diode emitters at 670 nm.
An Optically active compound is a molecule that rotates the plane of polarisation of plane-polarised light when passed through it
The standard unit for polarimetry is dm (1 dm = 10 cm), which simplifies the SOR formula and ensures consistency.
Typically, a sodium lamp emitting monochromatic light at 589 nm (D-line) is used.
It is a physical property because it does not involve a chemical change, but it is specific to molecular structure (chirality).
Yes. Optical rotation varies with temperature, so measurements often include temperature and wavelength
Further Reading
Quick Links