
Our pharma training Programs for corporate teams set the standard in the industry. We provide customised corporate training solutions specifically designed for the pharmaceutical industry, supported by a flexible and value-driven discount structure. Share your team’s requirements with us, and we’ll deliver a tailored proposal that meets your objectives and maximises value.
Select from our curated list of training programs—or let us know your specific needs, and we’ll design a solution just for you.
9+ Best Pharma Training Programs for Corporate Teams
Choose the training programs that best suit your team’s needs from the list below, and let us know your preferences. At PharmaGuru, we are committed to delivering the highest quality training and support — ensuring the best service in the industry:
- Quality by Design (QbD) in Analytical Method Validation Training
- Quality by Design (QbD) in HPLC Method Development Training
- Analytical Control Strategy, Preparation & Implementation Training
- QbD-Based Chiral Method Development Training for Complex APIs
- Quality by Design Approach for Pharmaceutical Impurity Control Training
- Regulatory Deficiency Letter Handling Training (FDA / EMA / WHO)
- Pharmaceutical Analysis Cost Reduction Training
- Stability Study Design & Shelf-Life Evaluation Training
- OOS (Out of Specification) & OOT (Out of Trend) Investigation Training
- GLP (Good Laboratory Practices) in Pharmaceutical Development
Corporate Training Program Pricing – PharmaGuru
PharmaGuru offers high-impact corporate training programs tailored for the pharmaceutical industry. Our group pricing model ensures value and flexibility for organisations of all sizes. Below is the standard pricing structure for each course, suitable for up to 10 participants.
Pricing Table
| Course Title | Price (Up to 10 Participants) |
|---|---|
| QbD in Analytical Method Validation | ₹35,000 |
| Handling Chiral Complexities using QbD | ₹35,000 |
| QbD Approach in HPLC Method Development | ₹35,000 |
| Analytical Control in APIs | ₹35,000 |
| QbD in Control of Pharmaceutical Impurities | ₹35,000 |
| How to Avoid/Handle Deficiency Letters | ₹35,000 |
| How to Reduce Pharmaceutical Analysis Cost | ₹35,000 |
| Stability Study and Shelf-life Evaluation | ₹35,000 |
| Handling OOS and OOT in Pharmaceuticals | ₹35,000 |
| GLP in Pharmaceutical Development | ₹35,000 |
Customise Your Learning Experience
| Add-On Options | Notes |
|---|---|
| 🔹 In-Person Delivery: +₹10,000 to ₹20,000 🔹 Customized Case Studies: +₹5,000 🔹 Post-Training Certification: +₹3,000 to ₹5,000 🔹 Extended Duration (2+ Days): +₹35,000 per day | 🔹 In-Person Delivery: +₹10,000 to ₹20,000 🔹 Customised Case Studies: +₹5,000 🔹 Post-Training Certification: +₹3,000 to ₹5,000 🔹 Extended Duration (2+ Days): +₹35,000 per day |
Ready to Train Your Team?
»Request a Quote
Inside Our Specialised Corporate Training Programs: Key Takeaways & Outcomes
See a concise summary of the key takeaways from each of our specialised training programs — carefully designed to align with industry best practices and global regulatory standards:
1. Quality by Design (QbD) in Analytical Method Validation Training:
Key Learnings
- Defining the Analytical Target Profile (ATP) & Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) to link method performance to what is required for safety, efficacy, and compliance.
- Use of risk assessment tools to identify critical method parameters (CMPs) / variables that significantly affect method performance.
- Design of Experiments (DoE) to explore method parameter space, understand interactions, optimize across multiple variables rather than one at a time.
- Establishing Method Operable Design Region (MODR) or design space, so that small changes in method parameters still yield acceptable performance.
- Lifecycle management: ongoing verification of method performance, dealing with drift, ensuring robustness over time, method transfer, and revalidation when required.

2. Quality by Design (QbD) in HPLC Method Development Training
Key Learnings
- Defining performance requirements (e.g. resolution, sensitivity, specificity, sample throughput) via ATP.
- Risk assessment to identify which HPLC parameters (mobile phase composition, pH, flow rate, column temperature, gradient vs isocratic, etc.) are critical.
- Use of DoE / factorial experiments to explore parameter interactions and optimise method.
- Establishing robustness & design space / MODR such that the method is tolerant to small variations without failing.
- Validation of the optimised method (linearity, accuracy, precision, LOD/LOQ, specificity, etc.) plus establishing a control strategy/monitoring plan for ongoing performance.
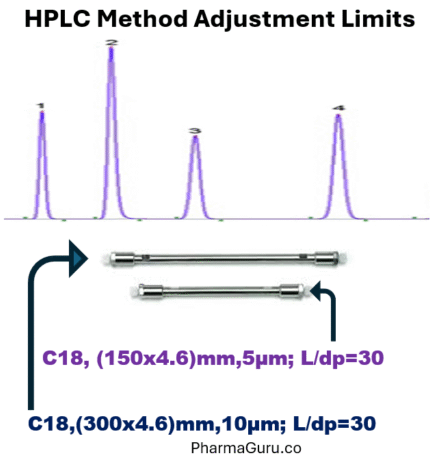
3. Analytical Control Strategy Development, Preparation & Implementation Training
Key Learnings
- Defining what needs to be controlled: identity, purity, potency, impurities (known & unknown), enantiomeric purity (if applicable), stability.
- Developing appropriate analytical methods for each control point, validated and robust.
- Risk‑based setting of specifications: what limits, what acceptance criteria, based on data, safety, potency, and regulatory expectations.
- Ensuring traceability and documentation: raw materials, intermediates, final API; auditing methods; sample stability; data integrity.
- Continual monitoring: stability, batch‑to‑batch variation, trends; establishing in‑process controls; whenever process or source changes, re‑evaluating control.
4. QbD-Based Chiral Method Development Training for Complex APIs
Keay Learnings
- Understanding stereochemistry: recognizing when APIs are chiral (multiple stereocenters, enantiomers, diastereomers) and their impact on pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, safety.
- Strategies for separation / resolution: choice of chiral stationary phases, chiral selectors, enantiomeric enrichment (synthesis or separation), use of chromatography, HPLC‑CSP etc.
- Applying QBD tools to chiral method development: define chiral CQAs (e.g. enantiomeric purity, resolution, tailing), CMPs (temperature, mobile phase, pH), DoE to optimize separation and resolution.
- Regulatory and control strategy for chiral impurities: setting specification limits, detecting minor enantiomer, monitoring, validation, ensuring compliance
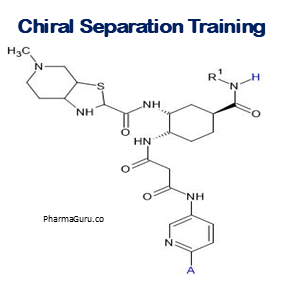
5. Quality by Design Approach for Pharmaceutical Impurity Control Training
- Control strategy: monitoring during manufacturing and storage, specification / in‑process control, stability studies, knowing when to take corrective actions.sures data integrity, product quality, and regulatory adherence.
- Classification of impurities: known vs unknown; genotoxic, mutagenic, degradation products; stereoisomeric impurities.
- Risk assessment to identify which impurities are critical (e.g. toxicity, amount, potential exposure).
- Analytical methods for impurity detection and quantitation: sensitivity (LOD/LOQ), specificity, resolution from main drug peaks; method validation.
- Defining acceptable impurity limits; justification based on safety data, ICH guidelines, trend analysis…….
6. Regulatory Deficiency Letter Handling Training (FDA / EMA / WHO)
- Good communication & timely response: when deficiency letters arrive, respond specifically, clearly, with corrective action plans, timelines, and evidence.
- Prior and thorough document review: ensuring accuracy, completeness, no typographical / structural / calculation errors in submissions.
- Understanding regulatory expectations and guidelines (ICH, regional) is especially important for impurities, analytical data, characterisation, etc., so that specifications are rational.
- Maintaining a deficiency letters database or lessons‑learned system: learn from what others have had, avoid repeating mistakes.
- Ensure all test methods, analytical procedures, validations are robust, documented, and justification is provided, especially for specification limits, impurity thresholds…….
7. Pharmaceutical Analysis Cost Reduction Training
- Use of QBD / DoE up front to optimize methods so that they are robust, fast, minimal solvent / reagent consumption, minimal re‑runs.
- Selecting methods / instrumentation that balance sensitivity with cost: maybe using simpler detectors, alternative techniques if sufficient.
- Reducing sample preparation steps, automating or simplifying them, pooling where feasible.
- Lifecycle approach: revalidating only when needed; monitoring method drift to avoid waste; method transfer efficiencies.
- Economies of scale: batch testing, reuse of validated methods across similar products, standardisation of methods, sharing controls etc.

8. Stability Study Design & Shelf-Life Evaluation Training
- Designing stability protocols as per ICH guidelines (conditions: temperature, humidity, light etc.), selecting relevant time‑points.
- Identifying degradation pathways, critical stability factors, and monitoring both API and impurities/degradation products.
- Setting shelf life based on real data: extrapolation only when justified, using statistical tools; considering storage conditions (packaging, etc.).
- Analytical method suitability: validated stability indicating methods, ability to detect degradation products, potency loss.
- Monitoring in real time and accelerated conditions; stability commitment post approval; re‑assessment when any change (formulation, process, packaging, storage).
9. OOS (Out of Specification) & OOT (Out of Trend) Investigation Training
- Clear definitions and SOPs for what constitutes OOS vs OOT; distinction is crucial.
- Investigation processes: immediate containment, root cause analysis, trending, corrective & preventive actions.
- Data integrity and documentation: ensuring sample handling, analyst procedures, instrument functionality, etc. are sound.
- Use of statistical tools/trend analysis to distinguish between lab error, method drift, and material issue.
- Preventive measures: robust method, routine monitoring, control strategy, calibration and maintenance, training.
10. GLP (Good Laboratory Practices) in Pharmaceutical Development
- Understanding GLP principles: organisation, personnel, SOPs, material controls, equipment, reagents, calibration, traceability.
- Ensuring documented and validated methods, instruments, proper sample handling, chain of custody.
- Quality assurance / GLP compliance: internal audits, record keeping, archiving, report integrity.
- Safety, environment, ethical practices (animal studies if any), responsibilities.
- Dealing with non‑compliance: reporting, corrective actions, and preventing recurrence.
»Hear What Our Learners Say About PharmaGuru
